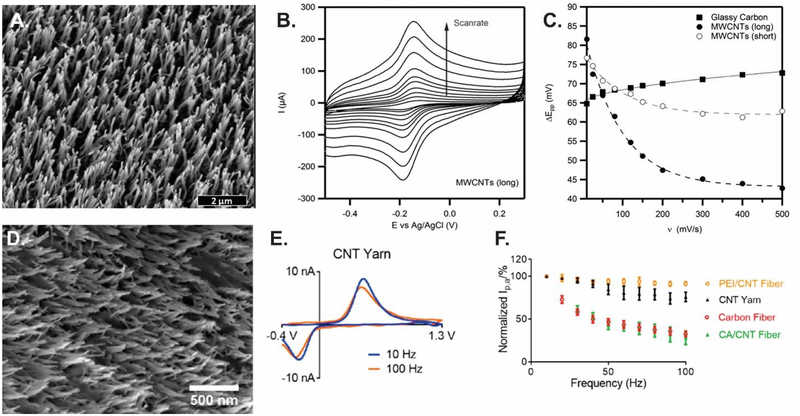
Fig. 6.
Thin layer effect studies in CV and FSCV. (A) 3 μm long MWCNTs modified GCE; (B) Scan rate study of 1 mM Ru(NH3)6Cl3; (C) Peak-to-peak separation vs. scan rate. The distance between the peaks is much smaller with long MWCNTs because the analyte is trapped at time scales of fast experiments. (D) CNT-yarn microelectrode; (E) Effect of scan repetition frequency for 1 μM dopamine detection at the scan repetition frequency of 10 Hz (blue) and 100 Hz (orange); (F) Peak oxidation current vs. frequency at different microelectrodes. Polyethyleneimine (PEI)-CNT and CNT yarn electrodes act as thin layer cells, which makes them nearly frequency independent, while carbon fibers and chlorosulfonic acid (CA)-CNT fibers are not thin-layer cells and are frequency independent. (A)-(C), Reprinted from Ref.138 with permission from Elsevier. (D)-(F), Reprinted from Ref.22 with permission from Elsevier.