Figure 2.
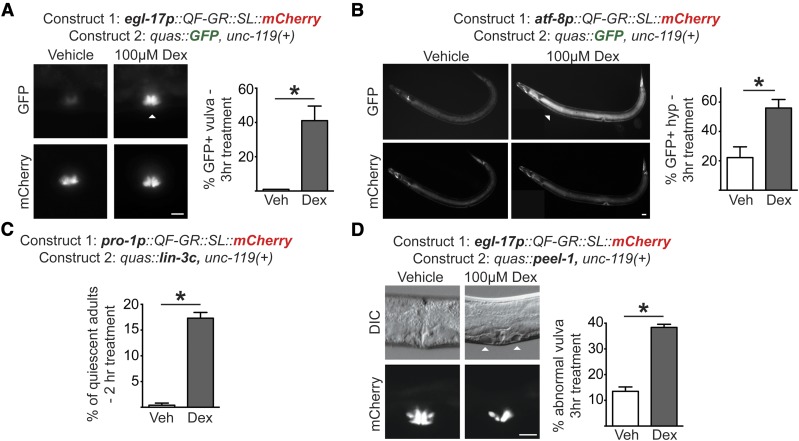
The QF-GR activator drives expression of target genes in various tissues. (A and B) Tissue-specific expression from the QF-GR activator in the (A) vulva or (B) hypodermis using the egl-17 or atf-8 promoters, respectively. The QUAS reporter contains the GFP gene. Representative fluorescent micrographs of GFP and mCherry expression from animals carrying the indicated transgenes and treated with vehicle or 100 μM dex for 3 hr. ▵’s denote the tissue-specific expression of GFP. To the right of each set of images is a bar graph denoting the average percentage of GFP-positive animals after an acute 3 hr vehicle or dex treatment (± SEM; n ≥ 25 animals). * P < 0.02, t-test. Bar, 20 μm. (C) Induction of lin3c/EGF induces behavioral quiescence in adult animals. QF-GR::SL::mCherry was expressed using the ubiquitous pro-1 promoter and the QUAS reporter contains the lin-3c gene. The graph depicts the percentage of quiescent adult nematodes after 2 hr of dex treatment. Behavioral quiescence of each animal was scored by two criteria: (1) the cessation of body movements for at least 30 sec, and (2) the absence of pharyngeal pumping for 60 sec. n ≥ 180 adults; * P < 0.005, t-test. (D) QF-GR::SL::mCherry was expressed using the egl-17 promoter, which is expressed primarily in vulval cells, and the QUAS reporter contains the peel-1 toxin gene. (Left) Induction of the peel-1 gene by dex in vulval cells. Representative Nomarski micrographs of vulvae in late L4 larvae treated with vehicle or 100 μM dex for 3 hr. ▵’s mark holes in the vulva of a dex-treated animal due to presumed cell death; fluorescent images depict the vulva-specific expression of mCherry. (Right) The graph depicts the average percentage of L4s and young adults with abnormal vulval morphology after an acute 3 hr vehicle or dex treatment (± SEM; n ≥ 279 animals for each condition). * P < 0.0001, t-test. Bar, 20 μm. DIC, differential interference contrast; Veh, vehicle.