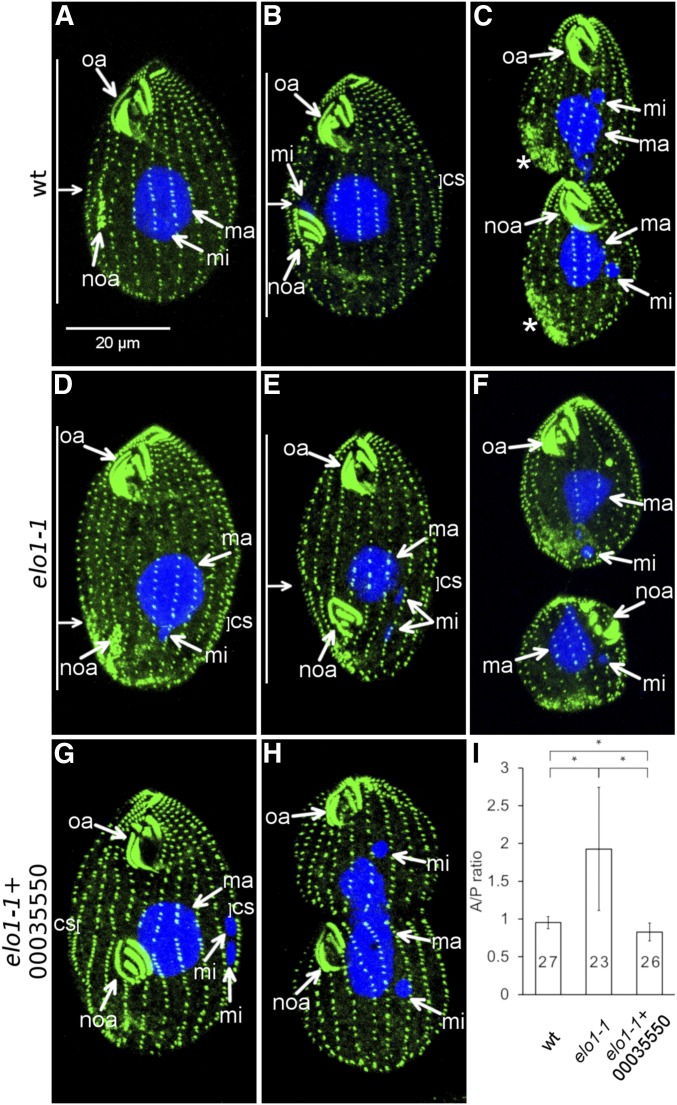
Figure 2.
elo1-1 shifts the division plane to the posterior cell end and expression of a wild-type THERM_00035550 protein rescues this defect. (A–F) The course of cell division in the wild type (A–C) and elo1-1 (D–F). The cells were labeled with the anti-centrin antibody (green) and DAPI (blue). The anti-centrin labels the basal bodies; in addition in some dividing cells these antibodies mark the vicinity of the contractile vacuoles [stars in (C)]. (A and D) Cells in the earliest stage of cell division (stage 1 in Figure 1A). Note that the oral primordium (noa) is sub-medial in the wild type (A) and excessively posterior in elo1-1 (D). (B and E) Cells during cortical subdivision (stage 4). (E). The micronucleus (mi) in the elo1-1 cell (E) is in a more advanced stage of mitosis as compared to the wild-type cell shown in (B). (C and F) Cells undergoing cytokinesis and amitosis of the macronucleus [the elo1-1 cell shown in (F) is in a more advanced stage]. (G–I) Introduction of a transgene expressing the GFP-TTHERM_00035550 rescues the unequal division in elo1-1 cells. (G and H) Dividing elo1-1 cells that carry the MTT1-GFP-THERM_0035550 transgene (grown without added cadmium ions). (I) The graph quantifies the position of the division plane as the ratio of the length of the presumptive anterior daughter to the length of the presumptive posterior daughter (the A/P ratio). Numbers of scored cells are indicated. Error bars are SD and asterisks show significant differences (two-sided t-test, P < 0.01). oa, oral apparatus; noa, new oral apparatus (primordium); ma, macronucleus; mi, micronucleus; cs, cortical subdivision. On the left side of (A, B, D, and E): the horizontal arrow indicates the position of the division plane and the vertical bars mark the lengths of the presumptive daughter cells.