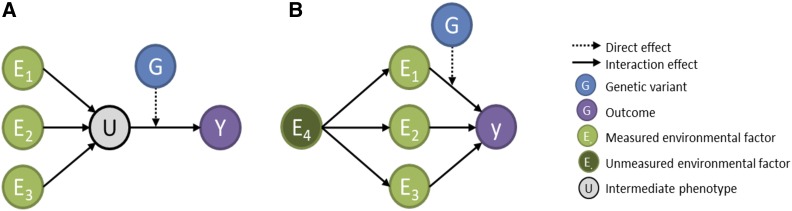
Figure 1.
Hypothetical causal model. In (A), multiple exposures (E1, E2, and E3) influence an intermediate phenotype (U), which effect on the outcome (Y) depends on a genetic variant (G). This scenario induces multiple interaction effects between G and the multiple exposures on the Y. In (B), multiple exposures (E1, E2, and E3) are influenced by another unmeasured variable, inducing a correlation between them. However, only one of these exposures interacts with G. In such case, the joint test of all interactions is more powerful than the test of E1xG only.