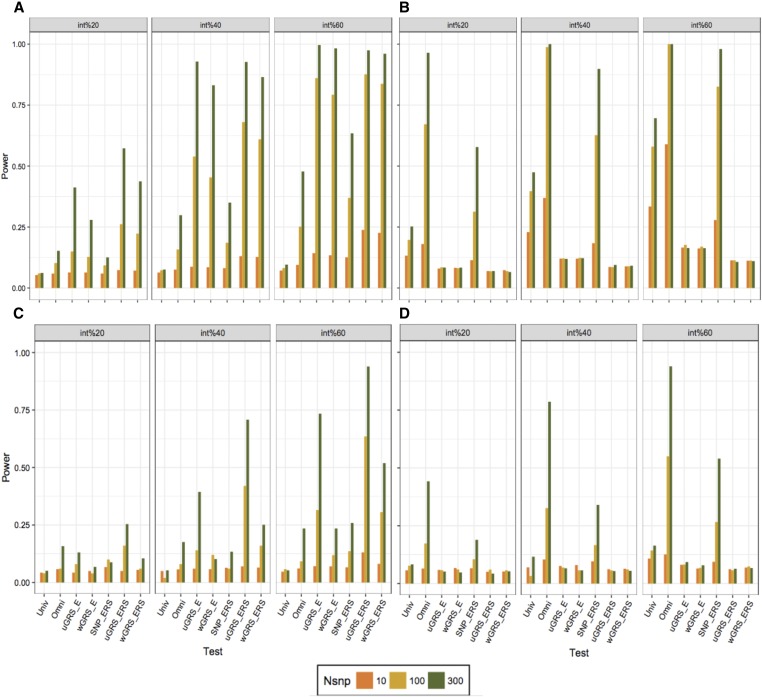
Figure 4.
Power comparison of G-E interaction approaches with normal distributed and highly correlated exposures. We derived series of 10,000 simulated replicates (except for univariate and omnibus tests in logistic models using 1000 replicates) and each included 20,000 samples, 10 exposures, and a varying number of SNP (n = 10, 100, and 300). (A) presents results for linear models assuming all G-E interactions effects correlated with marginal effects, (B) linear models assuming no correlations between G-E interaction effects and marginal effects, (C) logistic models assuming correlations between G-E interaction effects and marginal effects, and (D) logistic models assuming no correlations between G-E interaction effects and marginal effects.