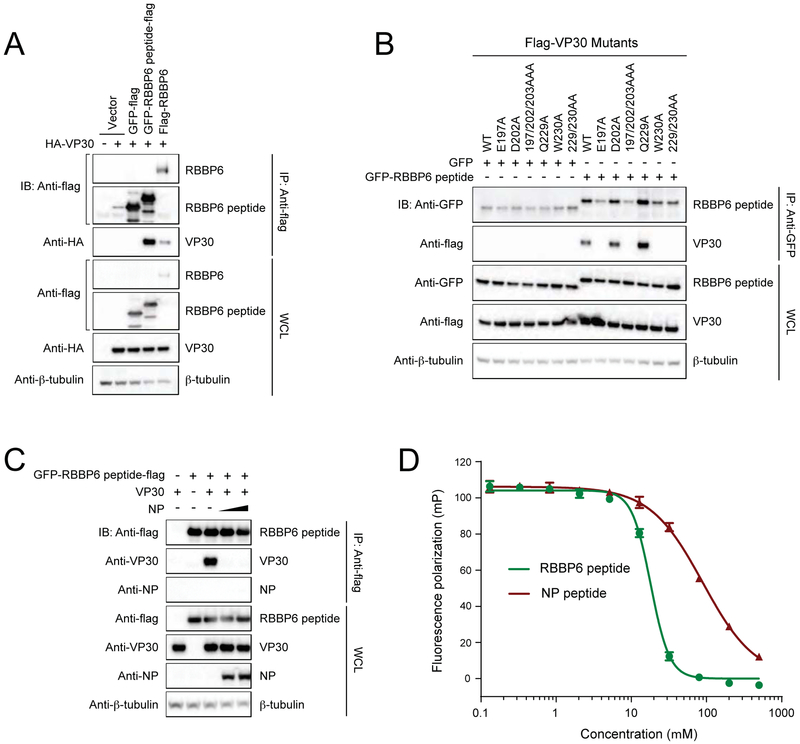
FIGURE 5. VP30 interacts with 549-571aa region of RBBP6.
(A) Representative immunoblots after Co-IP between HA-VP30 and RBB6P peptide fused to GFP-flag. GFP-flag was used as a control.
(B) Interaction between RBBP6 peptide and NP binding mutants of VP30.
(C) Co-IP experiment demonstrating that NP interferes with VP30-RBBP6 peptide interaction. IP was performed with anti-flag beads after co-expression of VP30, RBBP6 peptide fused to GFP-flag and NP. IP: immunoprecipitation; IB: immunoblot; WCL: whole-cell lysate.
(D) Fluorescence polarization assay showing RBBP6 peptide (green) displaces FITC-NP peptide (red) from the eVP30CTD-FITC-NP peptide complex. Error bars represent standard deviation of three independent experiments.