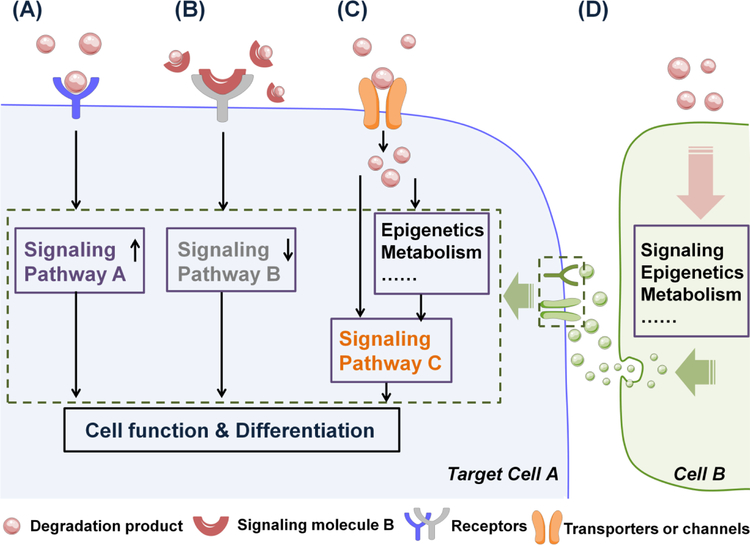
Fig. 5. The ways degradation products may link to cell function and differentiation.
(A) Degradation products may function as signaling molecules to promote signaling pathway A by interacting with cell membrane receptors, leading to altered cell function and differentiation. (B) Degradation products may interact with already known signaling molecule B to down-regulate signaling pathway B, which affecting cell function and differentiation. (C) Degradation products may enter cells via cell membrane transporters or channels to regulate cell functions directly or indirectly through signaling pathway C. (D) Degradation products may indirectly regulate target cell function and differentiation via modulating the paracrine signaling between target cell A and neighboring cell B.