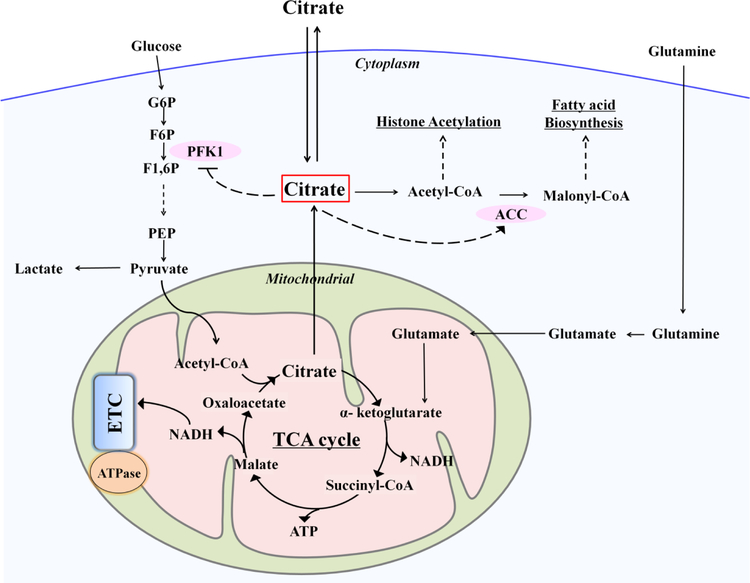
Fig. 6. Metabolic regulatory role of citrate in maintaining energy homeostasis.
Citrate locates at the crossroads of metabolism: is metabolized not only as an energy substrate in the TCA cycle to produce the majority of cellular ATP but also serves as a source of cytosolic precursor for fatty acid biosynthesis. Changes in citrate concentration could influence the activity of key enzymes: such as the PFK1 in glycolysis and the ACC in fatty acid synthesis. (PFK1, phosphofructokinase 1; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; F1,6P, fructose-1,6-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; ETC, electron transfer chain)