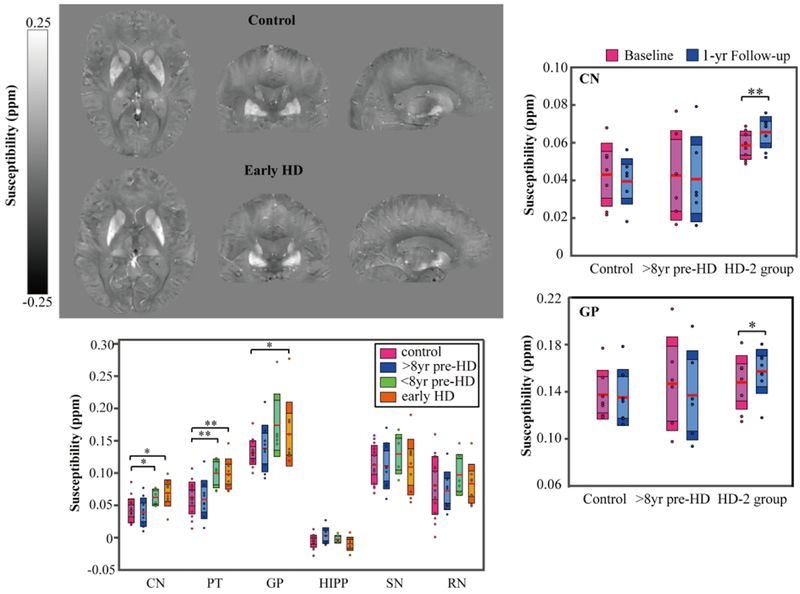
Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) was used to investigate altered brain iron content and iron deposition rate in Huntington disease (HD). Left top panel shows example QSM maps of a 61-yr-old female control as compared to example QSM maps of a 60-yr-old female early HD patients. Higher iron content in the striatum and pallidum were observed in the closer-to-onset premanifest HD and early-HD patients as compared to the control group, but not in the further-from-onset group (left bottom panel). In addition, significantly higher iron deposition rates in caudate and pallidum were firstly observed in closer-to-onset premanifest HD and early HD (HD-2 group) as compared to controls over one-year
