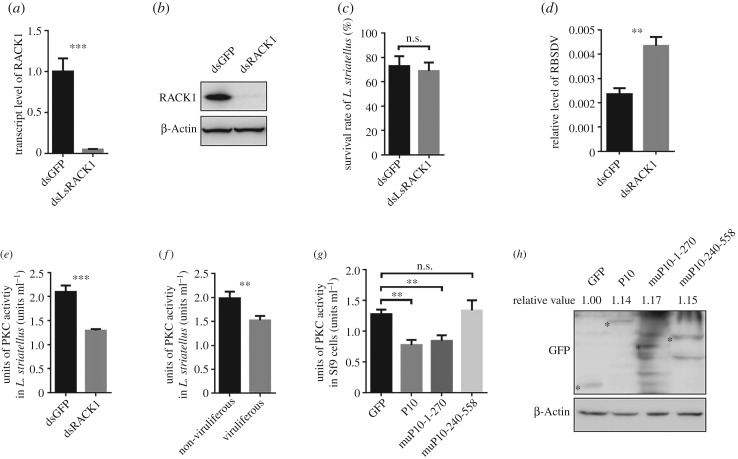
Figure 6.
LsRACK1 negatively regulated RBSDV accumulation in L. striatellus through suppressing the PKC signalling pathway. (a) Relative expression level of LsRACK1 in LsRACK1-dsRNA or gfp-dsRNA-microinjected L. striatellus at 48 h post-injection (hpi). Results were the means of 30 L. striatellus per treatment. (b) Western blot analysis of LsRACK1 in LsRACK1-dsRNA or gfp-dsRNA-microinjected L. striatellus at 48 hpi. The lower panel shows the accumulation of β-Actin and is used to show sample loadings. (c) Survival rates of LsRACK1-dsRNA or gfp-dsRNA-microinjected L. striatellus at 24 hpi. (d) Relative accumulation levels of RBSDV P10 in LsRACK1-dsRNA or gfp-dsRNA-microinjected L. striatellus at 15 d post virus acquisition. (e) Activities of PKC kinase in LsRACK1-dsRNA or gfp-dsRNA-microinjected L. striatellus. Thirty L. striatellus were used in each treatment. (f) Activities of PKC kinase in non-viruliferous and viruliferous L. striatellus. Each treatment had 30 L. striatellus. (g) PKC kinase activities in Sf9 cells expressing RBSDV P10, muP101-270, muP10-240-558 or eGFP. Bars in (a–g) are the means of three biological replicates ±s.d. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s., not significant difference (p > 0.05). (h) Western blot analyses of RBSDV P10-eGFP, muP10-1-270-eGFP, muP10-240-558-eGFP or eGFP expressed in Sf9 cells. The experiments presented in this figure were repeated three times. The relative expression levels of GFP, CP or CP mutants in each treatment were quantified using ImageJ software (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/). Mean values of target were obtained after normalizing to β-Actin control and the protein accumulation of GFP was set as standard ‘1’.