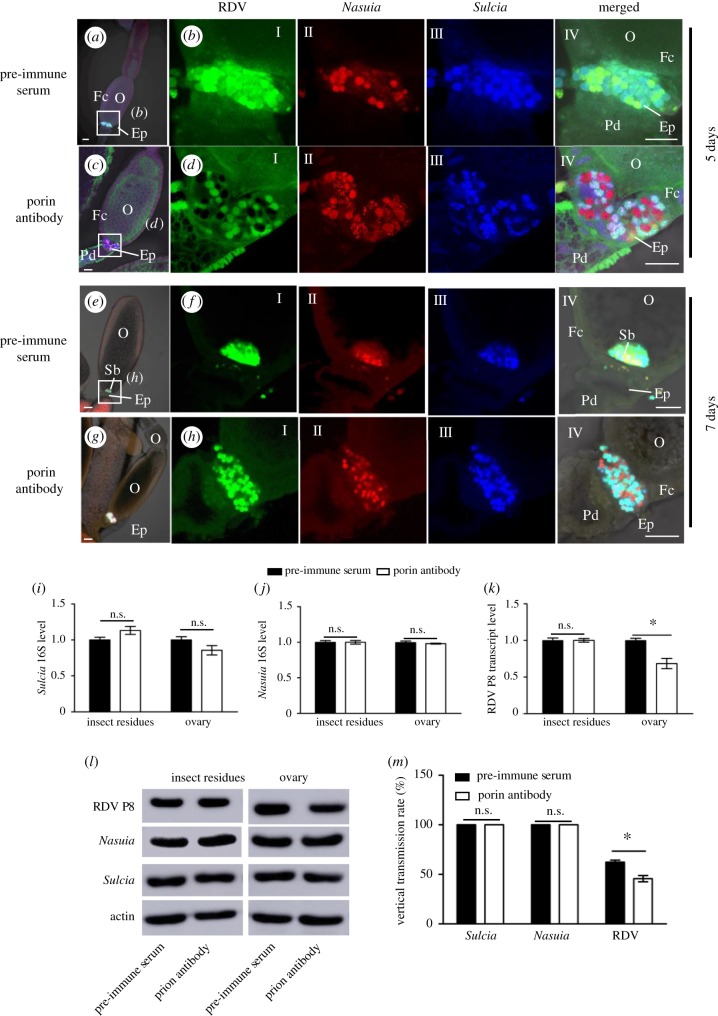
Figure 4.
Microinjection of Nasuia porin-specific antibody reduced RDV vertical transmission to the next insect generation. Newly emerged adult insects were injected with the purified RDV virions together with porin-specific antibody or pre-immune serum, and ovaries were dissected to detect RDV, Nasuia and Sulcia in 5 days. (a–d) At 5 days after microinjection, confocal micrographs showed the porin-specific antibody treatment inhibited the association of RDV with Nasuia, but not with Sulcia, in the epithelial plug. Scale bars: 100 µm. (e–h) At 7 days after microinjection, confocal microscopy showed that the Nasuia porin-specific antibody treatment strongly inhibited the association of RDV with Nasuia, but not with Sucia, in the ovaries. (i–k) Transcript levels of Nasuia 16S rRNA, Sulcia 16S rRNA and RDV P8 in ovaries or other parts of insects treated with porin-specific antibody or pre-immune serum, as determined by RT-qPCR assay in three independent experiments. (l) Accumulation levels of Nasuia, Sulcia and RDV P8 in ovaries or other parts of insects treated with porin-specific antibody or pre-immune serum, as determined by western blot using Nasuia porin-, Sulcia OMP- or RDV P8-specific IgGs, respectively. Insect actin was detected with actin-specific IgG as a control. (m) Vertical transmission rates of Nasuia, Sulcia and RDV after treatment with porin-specific antibody or pre-immune serum. Ep, epithelial plug; Fc, follicular cell; O, oocyte; Pd, pedicel. All images are representative of at least three replications. (i, j, k and m) Data are means ± s.e. from three independent experiments (independent-sample t-test at 0.05 level).