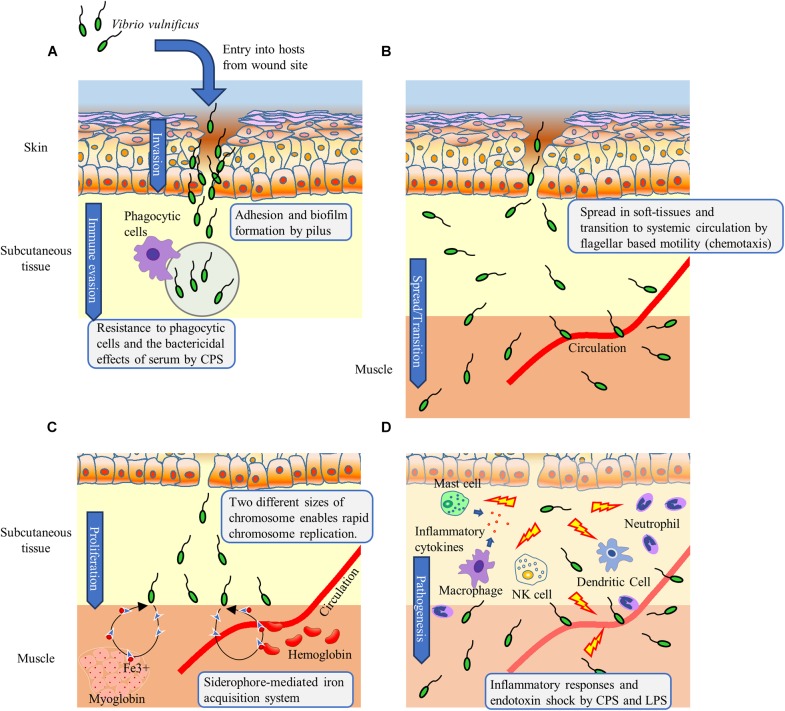
Figure 7.
STM screening reveals the essential factors whereby V. vulnificus invades, spreads, proliferates, and causes wound infection. (A) V. vulnificus adheres to cells located at the local wound infection site via the pilus. Biofilm formation and CPS contribute to resistance against immune cells. (B) V. vulnificus spreads in soft-tissues by flagellar based motility based on chemotaxis. (C) Two different sizes of chromosomes enable rapid chromosome replication leading to rapid cell division and proliferation. Iron, which is an essential element in bacterial metabolic and informational cellular pathways, is acquired via a siderophore-mediated system. (D) CPS and LPS induce inflammation-associated cytokines leading to septic shock.