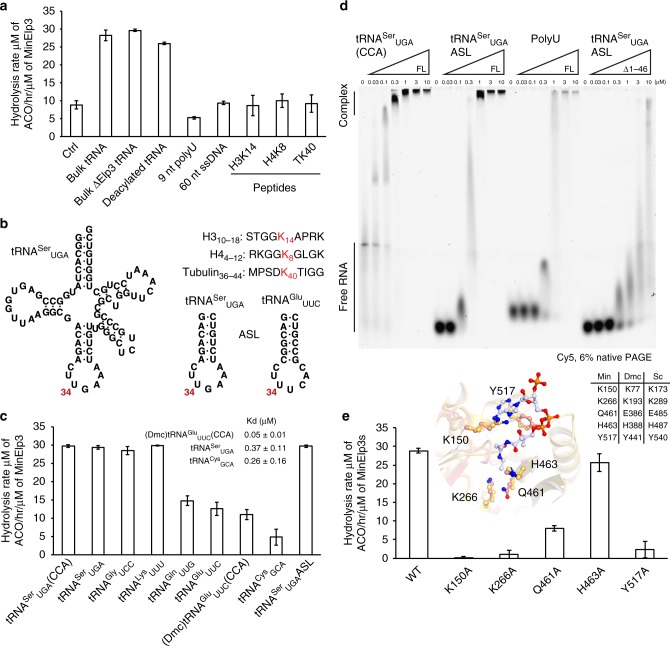
Fig. 4.
Substrate specificity feature of MinElp3 to activate acetyl-CoA hydrolysis. a Acetyl-CoA hydrolysis reactions of MinElp3 in the presence of different substrates, n = 3. b Chemical structure illustrations of tRNA and ASLs. Sequences of used peptides are given and modifiable lysine (K) residues are highlighted. c Acetyl-CoA hydrolysis reactions of MinElp3 in the presence of different tRNA substrates, n = 3 d EMSA analyses of MinElp3s binding to different nucleic acid substrates. Protein concentrations are given and positions of free tRNA and protein-tRNA complex are labeled. e Acetyl-CoA hydrolysis reactions of different MinElp3 point mutations in the presence of endogenous yeast bulk tRNA (Δelp3; UMY2916), n = 3. Superposition of highlighted residues in the acetyl-CoA binding pocket from MinElp3 (light pink) and DmcElp3 (yellow). DCA is shown in ball and sticks representation. The equivalent residue numbers in different Elp3s are indicated. Data represent mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file