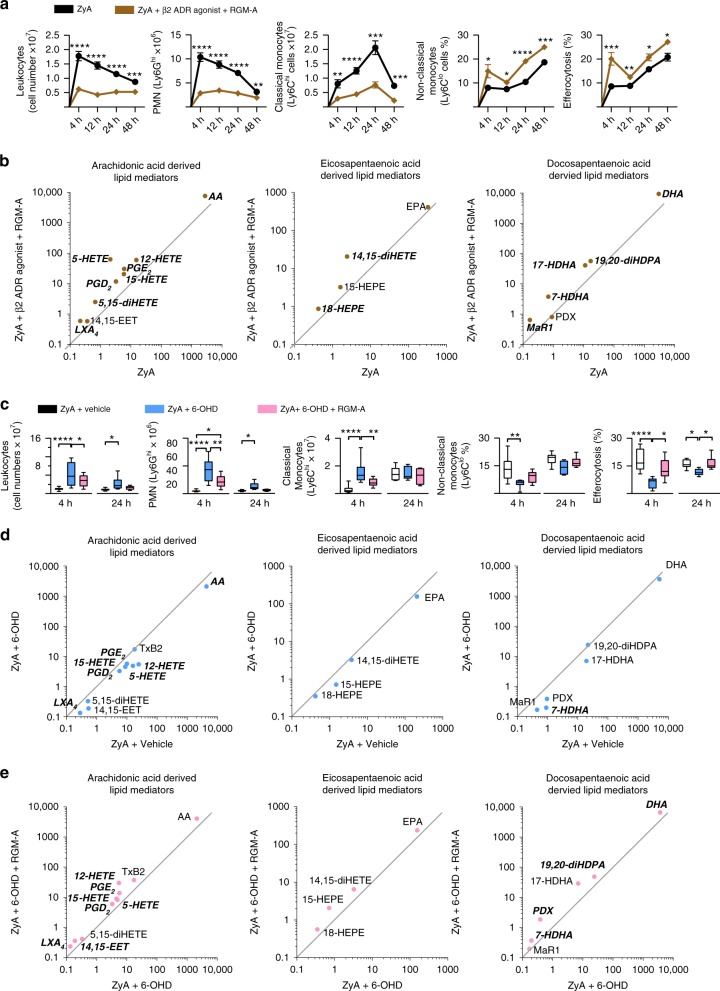
Fig. 4.
β2-adrenergic signaling and RGM-A synergistically activate inflammation-resolution programs. a, b WT animals were injected with ZyA and with vehicle or β2AR agonist and RGM-A, and lavages were collected at 4, 12, 24, and 48 h. a The total leukocytes were enumerated by light microscopy, and the PMNs, classical and non-classical monocytes as well as the MΦ efferocytosis by flow cytometry (n = 12). b Levels of bioactive lipid mediators and precursors including the AA, EPA and DHA pathway were quantified by LC-MS/MS-based profiling in peritoneal fluids of WT animals that were treated with ZyA and with RGM-A and Formoterol or vehicle for 4 h. Data are shown as the geometric mean in ng per 107 cells of peritoneal lavage and significant results are written in bold and italic (n = 10). c, d To induce a chemical sympathectomy WT animals were treated with 6-Hydroxydopamine hydrochloride (6-OHD) or vehicle 7, 5, 3 d before the ZyA and vehicle or RGM-A injections. Lavages were collected at 4 (n = 10) and 24 h (n = 7) and c total leukocytes were enumerated by light microscopy. PMNs, classical and non-classical monocytes as well as the MΦ efferocytosis were analyzed by flow cytometry. d Levels of bioactive lipid mediators and precursors including the arachidonic acid (AA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) pathway were quantified by LC-MS/MS-based profiling in murine peritonitis fluids that were treated with 6-OHD and vehicle or e) RGM-A for 4 h (n = 10). The results represent three independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SEM (a), geometric mean (b, d, e) and median ± 95% CI (c), unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (a, b, d, e), one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (c), *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001