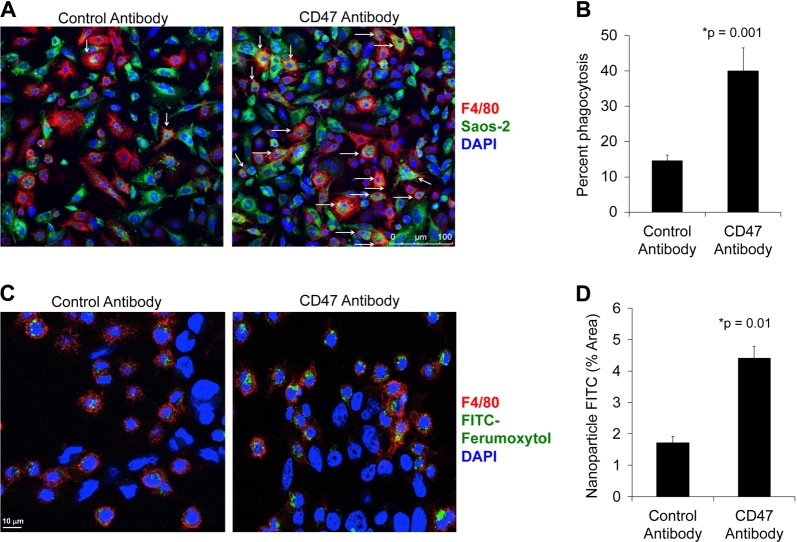
Fig. 2. CD47 inhibition triggers tumor cell and nanoparticle phagocytosis in vitro.
a Confocal images of CellBrite green-labeled Saos-2 tumor cells and F4/80+ murine macrophages in the presence of control IgG monoclonal antibody (mAb) (left) and CD47 mAbs (right; 10 μg/mL). CD47 mAb-exposed samples show an increased quantity of phagocytized tumor cells in macrophages (arrows; scale bar 100 μm). b Corresponding relative phagocytosis, calculated as the number of macrophages with phagocytized cancer cell divided by total macrophages per five high-power field × 100%. Data are displayed as means ± SD of n = 5 experiments per group, p = 0.001, exact two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. c Co-culture of F4/80+ macrophages, unlabeled MNNG/HOS cancer cells, and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-loaded ferumoxytol nanoparticles (scale bar 10 μm) in the presence of IgG control mAb or CD47 mAb. d Corresponding quantitative area of FITC stains in F4/80+ macrophages in control and CD47 mAb-treated samples for five high-power fields was measured using ImageJ. Results are represented as mean ± SD from five independent experiments, p = 0.01, exact two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum tests