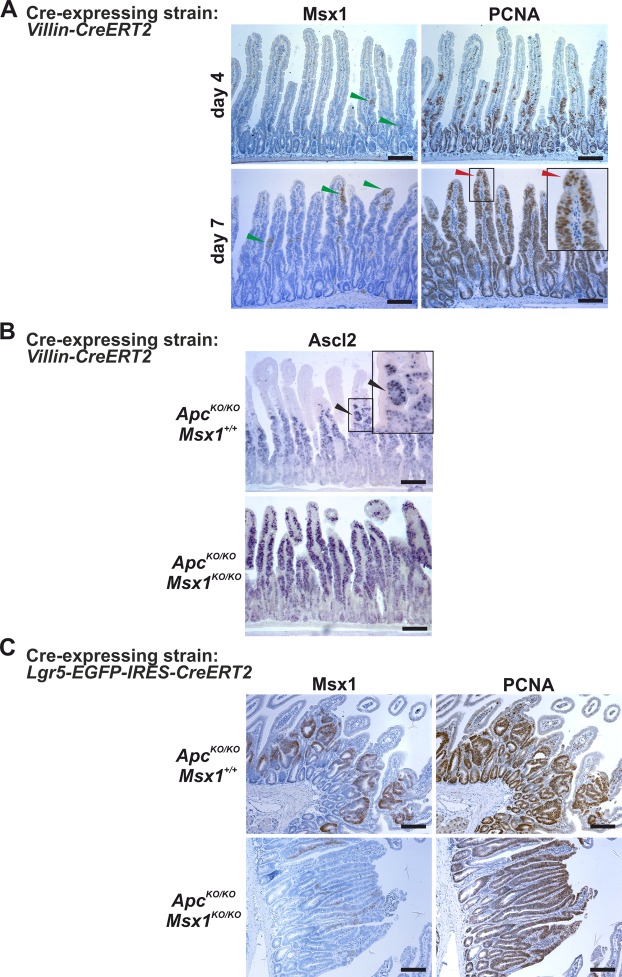
Figure 5.
Msx1 is essential for tubular morphology of early small intestinal adenomas. (A) Immunodetection of Msx1 and PCNA in ApccKO/cKO Msx1cKO/cKO Villin-CreERT2 mice at indicated time points after tamoxifen administration. At day 7, Msx1 depletion results in expansion of the proliferating cell compartments, and PCNA-positive cells reach tips of the villi (red arrowhead). Notice that the gene recombination is not complete and groups of Msx1-positive proliferating cells are occasionally detected on the villi (green arrowhead). (B) Detection of mRNA encoding stem cell marker Ascl2 in ApccKO/cKO Villin-CreERT2 (ApcKO/KO Msx1+/+) and ApccKO/cKO Msx1cKO/cKO Villin-CreERT2 (ApcKO/KO Msx1KO/KO) using ISH. The slides were processed 7 days after tamoxifen administration. Notice that an anti-sense Ascl2 probe robustly stains the hyperplastic and ectopic crypts developed on the villi (black arrowheads). (C) Msx1 loss alters morphology of Apc-deficient adenomas. Msx1 and PCNA immunohistochemical staining in neoplastic lesions developed in the small intestine of ApccKO/cKO Lgr5-EGFP-IRES-CreERT2 (ApcKO/KO Msx1+/+) and ApccKO/cKO Msx1cKO/cKO Lgr5-EGFP-IRES-CreERT2 (ApcKO/KO Msx1KO/KO) mice 21 days after tamoxifen administration. In contrast to the tubular adenoma developed in the mouse intestine with the intact Msx1 gene, the Msx1 deficiency results in formation of the villous type lesions. Sections in A and C were counterstained with hematoxylin. Boxed areas are magnified in the insets. The histological analysis was performed using samples obtained from ten animals (five for each genotype); representative images are shown. Additional sections are shown in Supplementary Fig. S6. The employed “Cre-deletor” mouse strains are indicated next to the corresponding images. Scale bar: 0.15 mm.