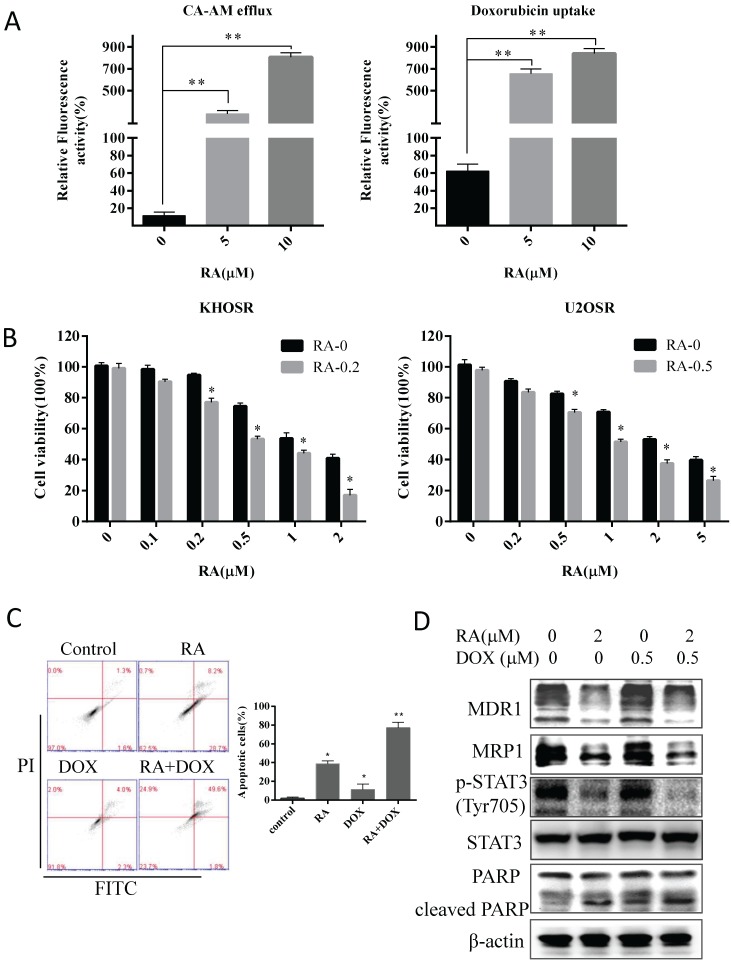
Figure 5.
RA reverses doxorubicin resistance in human OS cells by inhibiting STAT3 phosphorylation. (A) Cells were then treated with the indicated concentration of RA for 2 hours and then incubated with calcein AM for 30 min, calcein AM efflux was evaluated by green fluorescence observed using a fluorescence microscope and quantified by SpectraMax® M5/M5e plate reader. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of RA for 2 hours and doxorubicin, and doxorubicin uptake was evaluated by red fluorescence observed in fluorescence images and quantified by SpectraMax® M5/M5e plate reader. The cell nucleuses were stained by DAPI, which produced blue fluorescence. Relative fluorescence activity meaned the ratio of green (or red) quantity related to blue quantity. (B) KHOSR and U2OSR cells were treated with RA in combination with the indicated concentration of doxorubicin for 48 h, and cell viability was determined by CCK8 assay. (C) U2OSR cells were treated with or without doxorubicin pretreated with or without of RA for 2 h and then subjected to Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and flow cytometry analysis. (D) MDR1, MRP1, STAT3 phosphorylation, total STAT3, and cleaved-PARP expression were detected by immunoblotting in U2OSR cells treated with doxorubicin in presence or absence of RA. β-actin was used as a loading control. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with vehicle control.