Figure 1.
Axon Guidance Defects in the Nerve Bridge of Sox2 KO Mice
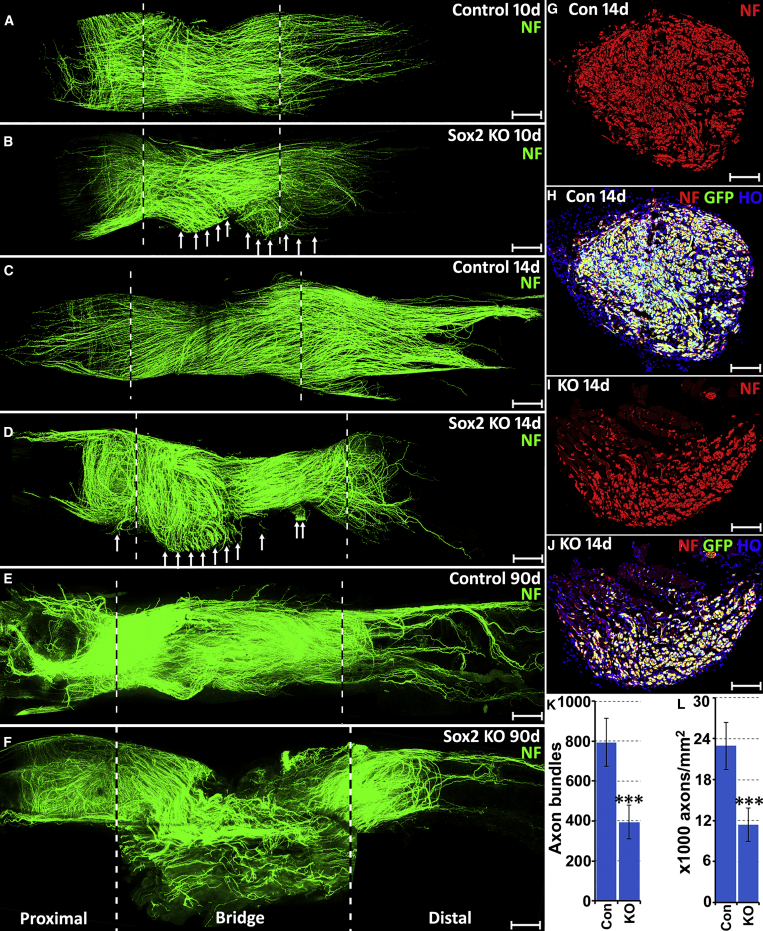
(A–F) Whole sciatic nerves stained with neurofilament (NF, green) antibody to show the pattern of regenerating axons in the nerve bridge of control and Sox2 KO mice at 10 (A and B), 14 (C and D), and 90 (E and F) days following transection injury. The nerve bridge is indicated between two dashed lines. Regenerating axons leaving the nerve bridge in Sox2 KO mice at 10 and 14 days are indicated by white arrows in (B) and (D). An unrepaired nerve bridge is still presented in Sox2 KO mice even at 90 days (F).
(G–J) Neurofilament (NF) antibody staining shows axon bundles (red) in the middle of the nerve bridge in control (G and H) and Sox2 KO mice at 14 days (I and J); Schwann cells are labeled with GFP in both control (H) and Sox2 KO (J) mice. Scale bar in (A–F) represents 300 μm and in (G–J) represents 6 μm.
(K and L) Quantification of numbers of axon bundles in the middle of the nerve bridge (K) and axon density (L) in the distal nerve stump of control and Sox2 KO mice. n = 3; ∗∗∗ indicate p < 0.001 compared with controls.
Several z series were captured on a Zeiss LSM510 confocal microscope in (A)–(F), covering the entire field of interest. The individual series were then flattened into a single image for each location and combined into one image using Adobe Photoshop software (Adobe Systems).