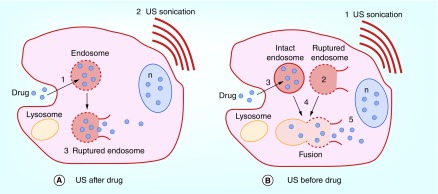
Figure 4. . Basic concept of sonochemical internalization of bleomycin.
(A) ‘Sonication after:’ cell membranes are loaded with an amphiphilic photosensitizer: (1) drug binds to the plasma membrane and it enters the cell together with the photosensitizer by endocytosis. The photosensitizer and the drug colocalize in the endosome, with the photosensitizer localized in the membrane and the drug in the lumen, (2) Exposure to FUS leads to, (3) sono-induced rupture of the endosome leading to the sequestered drug being released into the cell cytosol, entering the nucleus and thus inhibiting cell division; (B) ‘Sonication before:’ cell membranes are loaded with an amphiphilic photosensitizer: (1) FUS sonication, (2) FUS-induced disruption of endosome membrane containing photosensitizer, (3) Drug endocytosis and localization in intact endosomes, (4) Fusion of intact drug-containing and FUS-disrupted endosomes resulting in the sequestered drug being released into the cell cytosol, entering the nucleus and thus inhibiting cell division.
FUS: xxx; n: Nucleus.