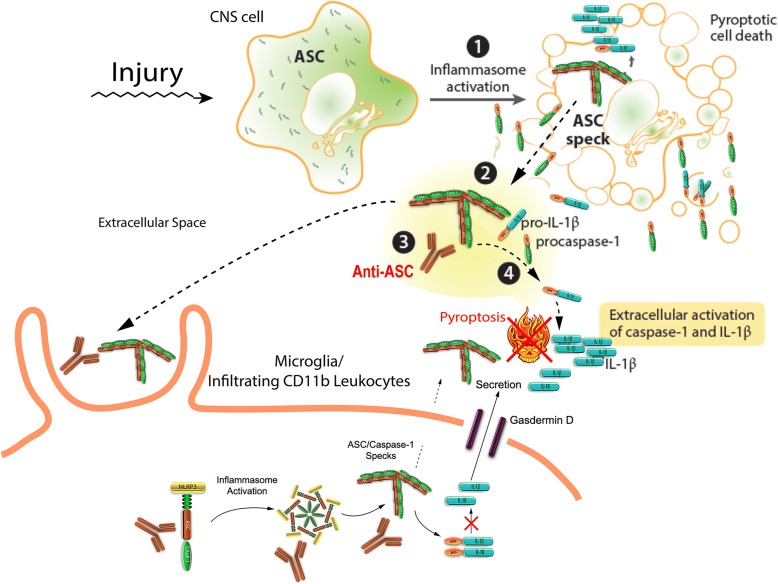
Fig. 5.
Schematic of inflammasome activation and pyroptosis of microglia after PBBI and proposed effects of anti-ASC on the pathway. CNS injury induces the formation of ASC specks in traumatized cells that are released into the extracellular space leading to maturation of IL-1β. ASC specks are taken up by endogenous microglia or infiltrating phagocytic cells resulting in further inflammasome activation and subsequent death by pyroptosis. Anti-ASC either binds to extracellular ASC specks blocking extracellular IL-1 maturation thereby decreasing inflammasome activation and pyroptosis of microglia and infiltrating CD11b leukocytes or binds to intracellular inflammasomes thereby leading to decreased activation and pyroptosis of microglia and infiltrating CD11b leukocytes. Adapted from Broderick et al. [25]