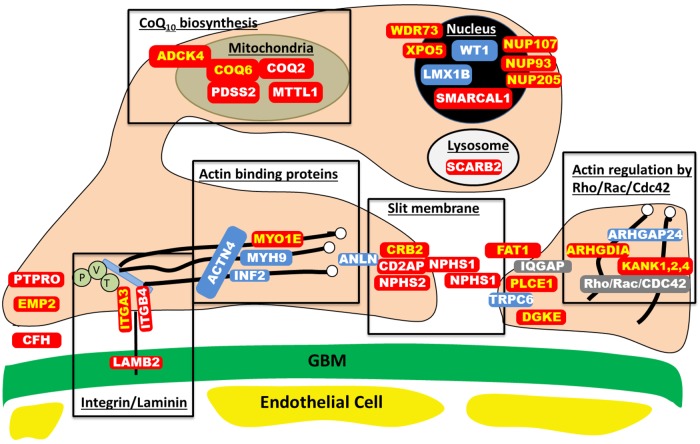
FIGURE 1:
Proteins involved in single-gene causes and pathogenic pathways of SRNS. Identification of single-gene (monogenic) causes of SRNS has revealed the renal glomerular epithelial cell, the podocyte, as the center of action in the pathogenesis of SRNS, because all of the related genes are highly expressed in podocytes. In this way, identification of genes that, if mutated, cause SRNS revealed certain proteins and functional pathways as essential for glomerular function, because a mutation in any single one of them is sufficient to cause SRNS. This figure depicts a simplified cross-section through two neighboring podocyte foot processes, which attach to the GBM via laminin/integrin receptors. Proteins that if mutated cause recessive monogenic forms of SRNS are in red, and proteins that if mutated cause dominant forms of SRNS are in blue. These SRNS-related proteins were found to be part of protein–protein interaction complexes that participate in defined structural components or signaling pathways of podocyte function (black frames). These proteins include: laminin/integrin receptors (focal adhesions), actin-binding proteins, glomerular slit membrane-associated components, actin-regulating small GTPases of the Rho/Rac/Cdc42 family, lyposomal proteins, nuclear transcription factors and proteins involved in coenzyme Q10(CoQ10) biosynthesis. Proteins that are encoded by recessive SRNS genes are marked in red: ADCK4, AarF domain containing kinase 4; ARHGDIA, Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) alpha; CD2AP, CD2-associated protein; CFH, Complement factor H; COQ2, coenzyme Q2 4-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyltransferase; COQ6, coenzyme Q6 monooxygenase 6; CRB2, Crumbs family member 2; DGKE, Diacylglycerol kinase, epsilon EMP2, epithelial membrane protein 2; GBM, glomerular basement membrane; ITGA3, integrin, alpha 3; ITGB4, integrin, beta 4; KANK, KN motif And Ankyrin Repeat Domains 1/2/4; LAMB2, laminin, β2; MTTL1, mitochondrial tRNA leucine 1; MYO1E, Homo sapiens myosin 1e; NPHS1, nephrin; NPHS2, podocin; NUP93, Nucleoporin 93 kDa; NUP107, Nucleoporin 107 kDa; NUP205, Nucleoporin 205 kDA; PDSS2, prenyl (decaprenyl) diphosphate synthase, subunit 2; PLCE1, phospholipase C, epsilon 1; PTPRO, protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, O; SCARB2, scavenger receptor class B, member 2; SMARCAL1, SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a-like 1; WDR73, WD repeat domain 73; XPO5, Exportin 5. Proteins that are encoded by dominant SRNS genes are marked in blue: ACTN4, actinin, alpha 4; ANLN, anillin; ARHGAP24, Rho GTPase-activating protein 24; INF2, inverted formin, FH2 and WH2 domain containing; LMX1B, LIM homeobox transcription factor 1-beta; MYH9, Myosin, heavy chain 9; TRPC6, transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6; WT1, Wilms tumor 1. IQGAP, IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1; P, Paxillin; V, Vinculin and T, Talin.