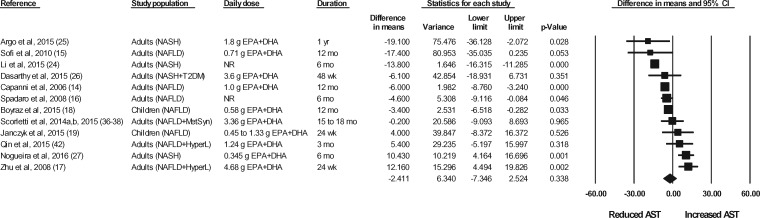
Figure 2.
Effects of n-3 LC-PUFAs vs a control on AST levels in patients with NAFLD. A random-effects model was used to calculate the pooled estimate of the differences in means and the accompanying 95%CI. Studies were weighted by the inverse of their variance; the area of each symbol is proportional to the weight of the study. The diamond represents the pooled effect. The pooled change from baseline in serum AST levels with intake of n-3 LC-PUFAs, corrected for changes from baseline in the control group, is −2.41 IU/L (95%CI, −7.35 to 2.52 IU/L; P=0.338). Using the trim and fill method of Duval and Tweedie,35 1 study was found to be missing to the right of the mean effect. With this study imputed, the pooled effect is −1.56 IU/L (95%CI, −6.47 to 3.35 IU/L). Abbreviations: AST, aspartate aminotransferase; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; HyperL, hyperlipidemia/dyslipidemia; n-3 LC-PUFAs, omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids; MetSyn, metabolic syndrome; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; NR, not reported; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.