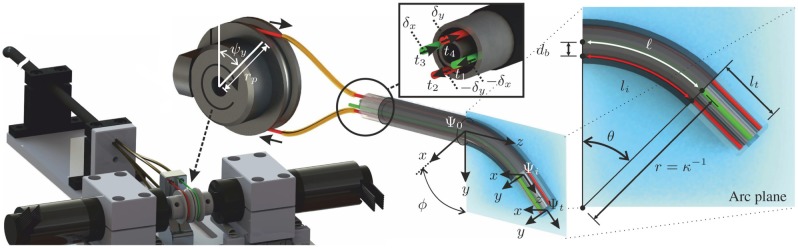
Fig. 2.
An overview of the robotically actuated delivery sheath (RADS). The articulating tip of the RADS is actuated in two degrees of freedom by two pairs (red and green) of antagonistic-configured tension wires driven by a two pulleys with radii () and angles ( and ). Three coordinate systems are assigned to describe the tip pose of the RADS: is the reference frame fixed to the shaft, is the intermediate frame assigned to the arc section and frame () is fixed to the articulating tip. Displacement of the tension wires () by and (inset centre) results in instrument bending along the x- and y-axes (frame ()), respectively. The arc of the RADS with parameters, bend angle (), backbone length (), radius (r) and curvature () lies in a plane described by the arc plane (inset right). The orientation of the arc plane about the z-axis of the reference frame () is denoted by angle (). Further, the tendon distance to the backbone arc () is denoted . A rigid link (not completely shown) of length () is attached to the arc (frame ()) of the RADS.