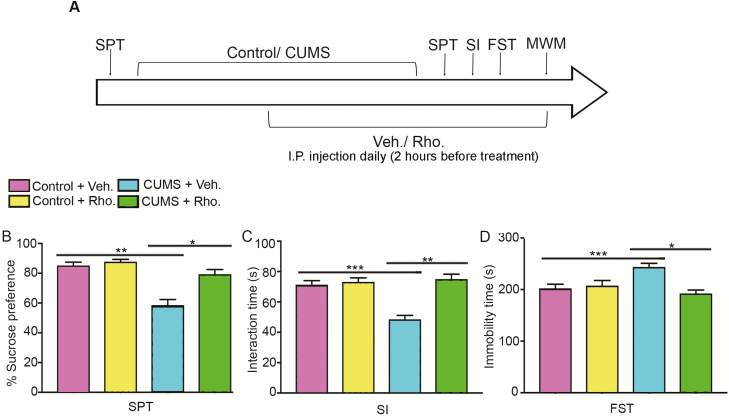
Figure 1.
Influence of rhodomyrtone administration on depression-like behaviors in chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS). (A) Schematic of the experimental design for assessing the effect of rhodomyrtone administration in CUMS mice on depression-like behaviors. Mice were subjected to CUMS for 5 weeks. Rhodomyrtone was i.p. injected during the last 3 weeks of CUMS. Behavioral tests were conducted after exposure to the CUMS protocol. (B) CUMS mice showed less sucrose consumption than the control mice. Rhodomyrtone treatment for 3 weeks reversed the decrease of sucrose consumption in CUMS mice. (C) Rhodomyrtone treatment increased interaction time in the CUMS group. (D) Rhodomyrtone inhibited the CUMS-caused increase of immobility time in the forced swim test (FST). n=9 for all groups; data are presented as mean±SEM; *P<05; **P<.01; ***P<.001.