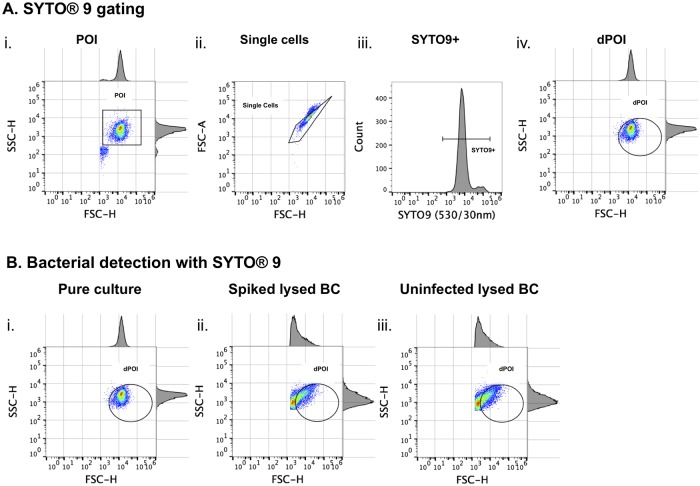
Fig 2. Bacterial detection by acoustic flow cytometry after direct staining with SYTO 9 in pure bacterial culture and inoculated blood culture.
A: SYTO 9 gating for bacteria grown in TSB as pure culture: the population of interest (POI) was gated based on the FSC-H/SSC-H scatter plot (i) while single bacterial cell events were identified in the FSC-H/FSC-A plot (ii). Events that were SYTO 9 positive were gated in the BL1-H channel (iii) and back-gated to FSC-H/SSC-H scatter plot to identify bacterial cells labelled with SYTO 9, denoted as derived POI (dPOI) (iv) since SYTO 9 binds to other particles containing nucleic acids. B: Bacterial detection in pure culture (i) and blood culture (ii) by SYTO 9 staining. Uninfected BC was used as a negative control (iii). Both pure culture (i) and blood culture (ii) were inoculated with identical concentrations of bacteria at approximately 8.00 x 104 CFU/mL. The pure bacterial culture was stained directly with SYTO 9, while both spiked and uninfected blood cultures were lysed with 10% Triton X-100 before SYTO 9 staining. Note the strong background noise produced during the BC lysis in both infected and uninfected BC samples overshadowing dPOI (ii and iii).