Figure 7.
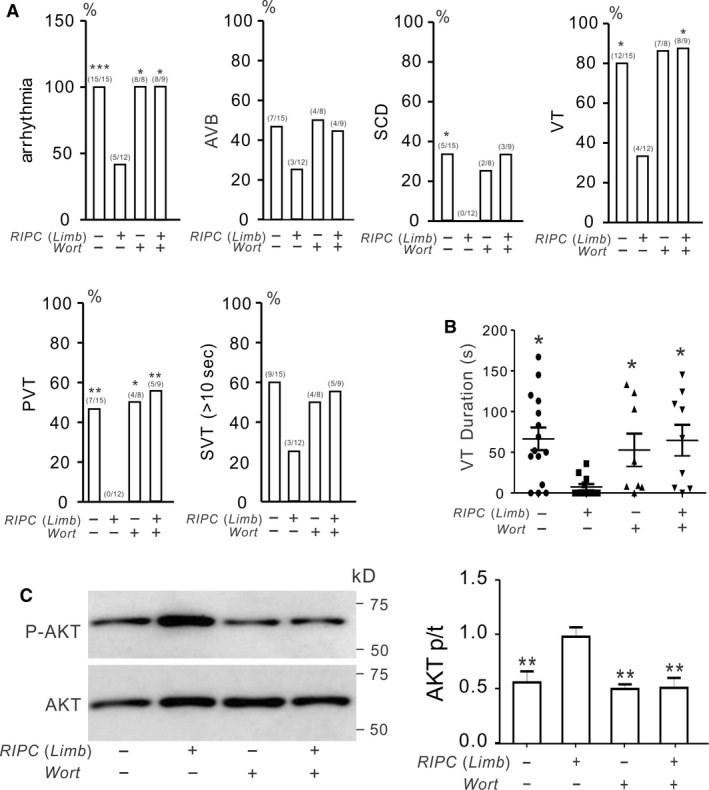
AKT phosphorylation is essential for remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC)‐limb‐induced antiarrhythmic activity in Kcne2‐/‐ mice post‐IR. (A) The effect of inhibiting AKT (Wortmannin, Wort) on postreperfusion arrhythmia characteristics in Kcne2 ‐/‐ mice in the absence (−) or presence (+) of limb I/R preconditioning stimulus. Values in parentheses indicate the numbers of mice per category. n = 8–15 each group. Values for Kcne2 mice without inhibitor are repeated from Figure 2 for comparison. AVB, AV block; SCD, sudden cardiac death; VT, ventricular tachycardia; PVT, polymorphic VT; SVT, sustained ventricular tachycardia over 10 sec. (B) Durations of VT for RIPC‐Limb‐treated or nontreated Kcne2 ‐/‐ mice in the presence (+) or absence (−) of AKT inhibitor Wortmannin (Wort) application. Mice without VT were indicated as 0 sec duration. Values for Kcne2 ‐/‐ mice without inhibitors are repeated from Figure 2 for comparison. *P < 0.05 versus Kcne2 ‐/‐ mice after RIPC‐limb treatment without inhibitor. (C) Left, typical blot of phospho‐(p) AKT and total (t) AKT from Kcne2 ‐/‐ mice with or without RIPC‐limb treatment in the presence (+) or absence (−) of AKT inhibitor Wortmannin (Wort) application. Right, mean ratio of band densities of pAKT/tAKT (n = 4–5 each group).*P < 0.01, versus Kcne2 ‐/‐ mice after RIPC‐limb treatment without inhibitors.
