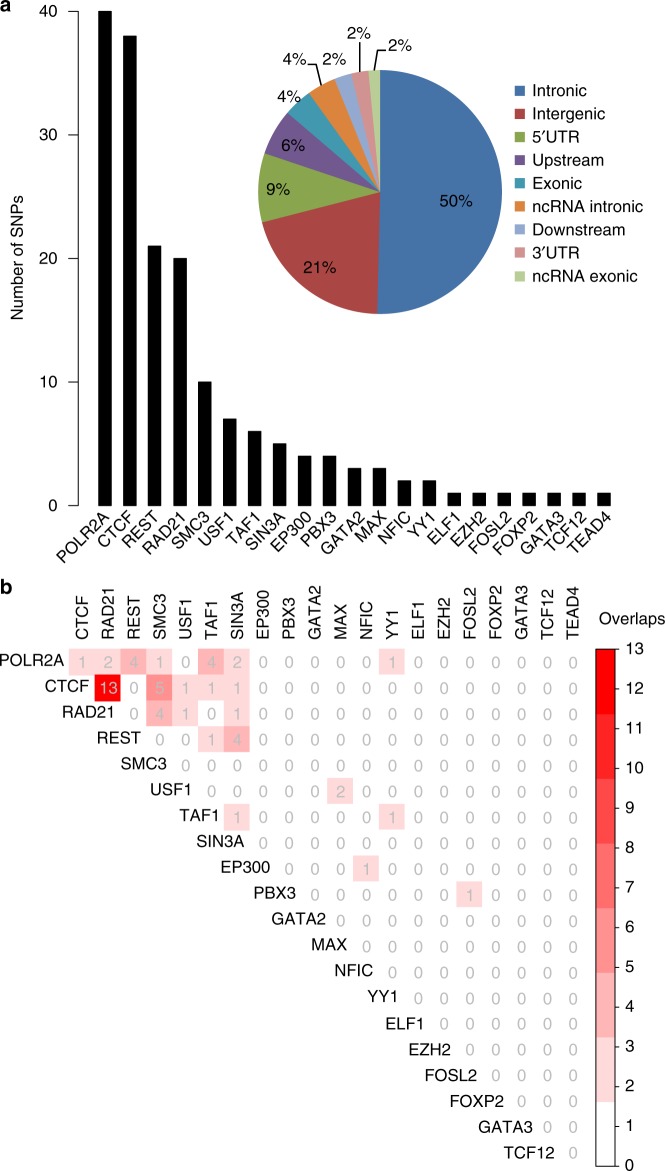
Fig. 3.
Transcription factors (TFs) disrupted by schizophrenia risk single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). a Left panel, The box plot shows the number of schizophrenia risk SNPs disrupting the binding of individual TF based on matched position weight matrices (PWMs) from chromatin immunoprecipitation and sequencing (ChIP-Seq) and PWM database. a Right panel, The distribution of the 132 identified TF binding–disrupting SNPs in the human genome. Most of the identified regulatory SNPs were located in intronic and intergenic regions. b The number of SNPs disrupting the binding of two TFs simultaneously. In addition to disruption of individual TF, we also found that some of the identified regulatory SNPs disrupt the binding of two TFs. Of note, 13 risk SNPs disrupted the binding of CTCF and RAD21 simultaneously