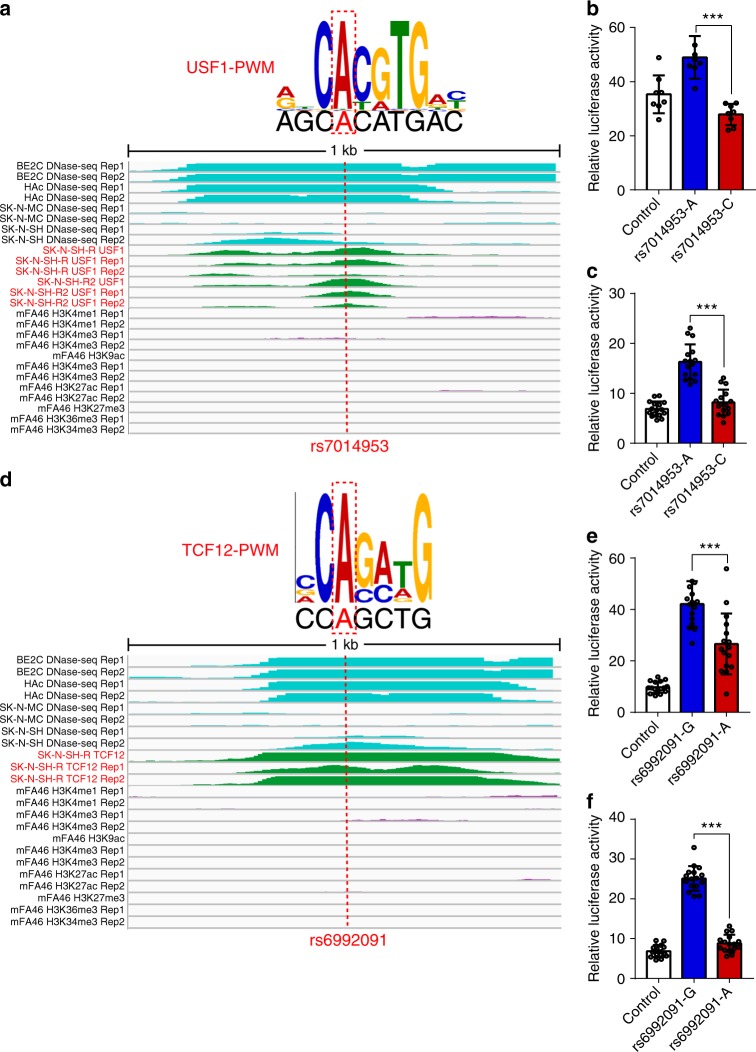
Fig. 7.
Disruption of USF1 and TCF12 binding by risk single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs7014953 and rs6992091. a SNP rs7014953 is located in binding motif of USF1 and disrupts occupied USF1 binding site. The matched position weight matrix (PWM) and the location of rs7014953 (red dotted line) are shown. DNase-Seq and chromatin immunoprecipitation and sequencing (ChIP-Seq) experiments showed that rs12912934 overlaps with DNase-Seq and ChIP-Seq peaks, indicating that USF1 can bind to the genomic region containing rs12912934 in human brain tissues or neuronal cell lines. b, c Reporter gene assay showed that the construct containing A allele (of rs7014953) exhibited significant higher luciferase activity compared with the construct containing the C allele in SK-N-SH (b) and SH-SY5Y (c) cells. d SNP rs6992091 is located in the binding motif of TCF12 and disrupts occupied TCF12 binding site in human brain tissues or neuronal cell lines. Matched PWM of TCF12 and the location of rs6992091 are shown (with red dotted box). Genomic region (1 kb) surrounding SNP rs6992091 is shown with three featured visualization tracks, including DNase-Seq signal (light blue), ChIP-Deq signal (green) for TCF12 and histone modifications (purple). The location of rs6992091 is highlighted with the dotted red line. e, f Reporter gene assay showed that the construct containing G allele (of rs6992091) exhibited significant higher luciferase activity compared with the construct containing the A allele in SK-N-SH (b) and SH-SY5Y (c) cells. Data represent mean ± SD; n = 8 for each group in b (SK-N-SH cells) and n = 16 for each group in c, f (SH-SY5Y cells) and e (SK-N-SH cells). ***P < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file