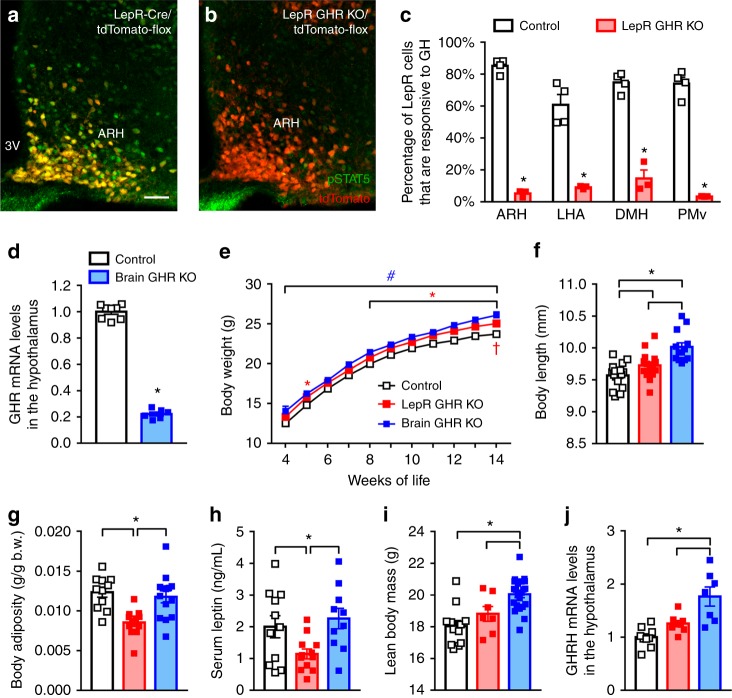
Fig. 5.
Consequences of growth hormone receptor (GHR) ablation in leptin receptor (LepR)-expressing cells or the entire brain. a–c A high percentage of LepR neurons (red) in the arcuate nucleus (ARH; t(5) = 28.42, P < 0.0001), lateral hypothalamic area (LHA; t(5) = 6.777, P = 0.0011), dorsomedial nucleus (DMH; t(5) = 10.51, P = 0.0001) and ventral premammillary nucleus (PMv; t(5) = 14.6, P < 0.0001) is responsive to porcine growth hormone (GH) (20 µg/g body weight (b.w.)) in control mice (phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (pSTAT5), green), whereas very few pSTAT5 is observed in tdTomato cells of LepR GHR KO mice (n = 3–4; unpaired t-test). Yellow represents double-labeled cells. Scale Bar = 50 µm. d GHR mRNA expression in the hypothalamus of control and brain GHR KO mice (t(12) = 30.02, P < 0.0001, n = 6–8; unpaired t-test). e Body weight changes in control, LepR GHR KO and brain GHR KO mice (main effect of time [F(10, 1036) = 370.9, P < 0.0001], main effect of GHR ablation [F(2, 1036) = 76.28, P < 0.0001] and interaction [F(20, 1036) = 0.4301, P = 0.9867]; two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA); n = 14–20; *P < 0.05, LepR GHR KO vs. control mice; #P < 0.05, brain GHR KO vs. control mice; †P < 0.05, LepR GHR KO vs. brain GHR KO mice). f Body length (F(2, 42) = 16.29, P < 0.0001, n = 13–17). g Body adiposity (F(2, 34) = 9.815, P = 0.0004, n = 11–14). h Serum leptin concentration (F(2, 30) = 4.477, P = 0.0199, n = 10–12/group). i Lean body mass (F(2, 38) = 13.17, P < 0.0001, n = 7–22/group). j Hypothalamic GHRH mRNA expression (F(2, 21) = 13.43, P = 0.0001, n = 7–9) of 6-month-old male mice. One-way ANOVA and the Newman–Keuls test were used when the data of control, LepR GHR KO and brain GHR KO mice were compared. All results were expressed as mean ± s.e.m.