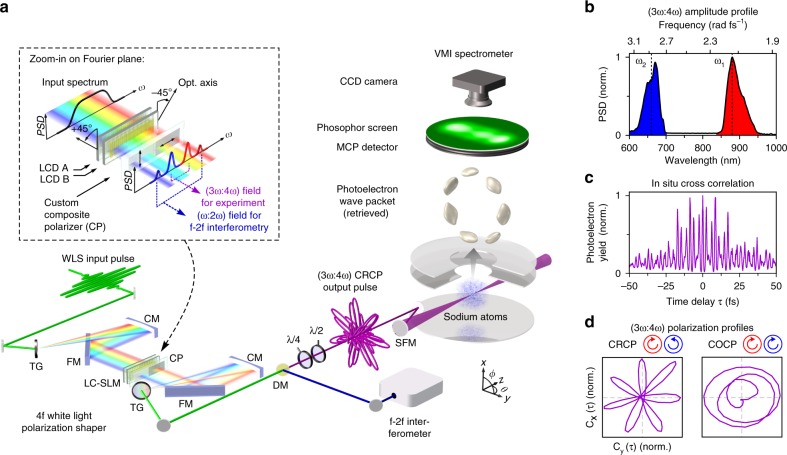
Fig. 1.
Experimental setup and pulse characterization. a The experimental setup combines shaper-based generation of (3ω:4ω) BiCEPS pulses and photoelectron tomography using a VMIS. Bichromatic amplitude, phase and polarization modulation is implemented by a 4f polarization pulse shaper, adapted to the over-octave spanning WLS and equipped with a composite (CP) polarizer in the Fourier plane9 (see inset). The additional optical elements are: transmission gratings (TGs), cylindrical mirrors (CMs), folding mirrors (FMs) and a quarter wave plate (λ/4). A multi-chromatic field is extracted from the WLS, consisting of the (3ω:4ω) BiCEPS pulse and an additional (ω:2ω) field for active CEP stabilization. The former is coupled into the VMIS via a spherical focusing mirror (SFM), while the latter is split off the main beam via a dichroic mirror (DM) to seed a single-shot f-2f interferometer11. 2D projections of the released FEWP are detected under various angles by rotating the BiCEPS pulse using a λ/2 wave plate. The 3D FEWP is retrieved by employing tomographic techniques10. b Measured amplitude profile of a shaper-generated (3ω:4ω) field. c In situ shaper-based CC trace9,11 from MPI of Na atoms with (3ω:4ω) PLP pulses. The trace shows the beating of the two colors. From the temporal width of the trace, we derive a pulse duration of Δτ1 = Δτ2 ≃ 25 fs. d Measured parametric first order CC trajectories9 visualize the polarization profile of the shaper-generated (3ω:4ω) BiCEPS fields. The CC trajectory of the CRCP field reveals a propeller-type profile with sevenfold rotational symmetry (left), while the trajectory of the COCP field yields a heart-shaped profile (right). For clarity, only the central beating cycle is displayed