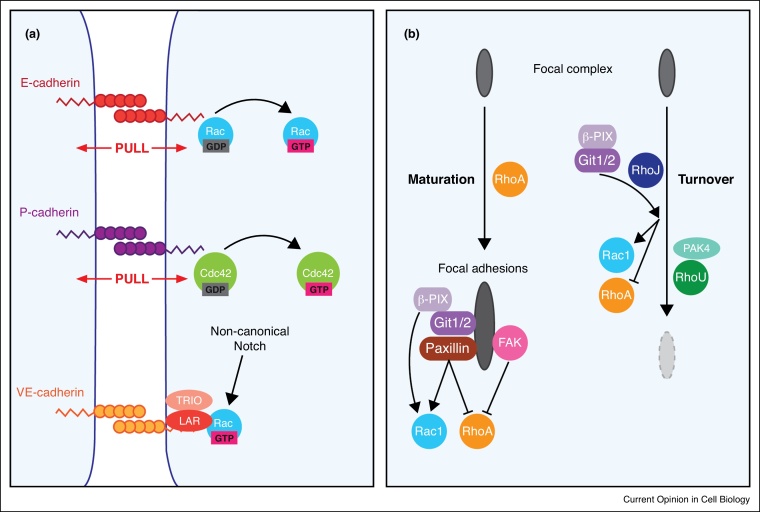
Figure 2.
Rho family GTPases in the context of adhesion. (a) Rac1 and CDC42 control the directionality of groups of migrating cells when activated via the mechanical stretch of E-cadherin and P-cadherin respectively. Non-canonical notch signalling leads to the formation of a VE-Cadherin-LAR-TRIO complex that leads to the activation of Rac1. (b) RhoA signalling can promote focal complex maturation, leading to the recruitment of integrin associated proteins. These proteins include the Git1/2-β-Pix complex that binds to paxillin and signals to promote Rac1 signalling and supress RhoA signalling. RhoJ can enhance focal complex turnover, by recruiting the β-Pix-GIT complex in order to block RhoA signalling, blocking RhoA mediated focal adhesion maturation. RhoU, when stabilised by PAK4 can also promote the turnover of focal adhesions.