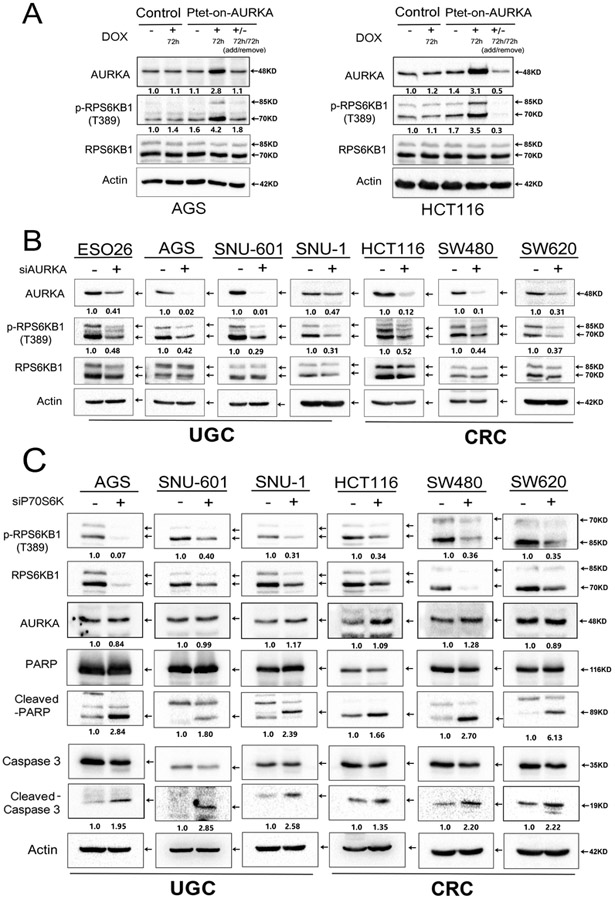
Figure 3. Genetic knockdown of AURKA suppresses phosphorylation of RPS6KB1 in GI cancer cells.
A, AGS and HCT116, cells stably expressing Tet-One™ inducible AURKA, were cultured in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml doxycycline for 72 hrs. Doxycycline-induced overexpression of AURKA led to an increase in p-RPS6KB1 (T389). B, Western blot analysis showing reduced protein levels of p-RPS6KB1 (T389), following siRNA knockdown of AURKA in GI cancer cells. C, Knockdown of RPS6KB1 using specific siRNA in GI cancer cells (AGS, SNU-601, SNU-1, HCT116, SW480, SW620). Western blot analysis demonstrates an increase in cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase 3, without altering the protein levels of AURKA. Representative blots are from one of three independent experiments with similar results. The relative density of bands are shown under the immunoblot after normalization to the levels of actin. Quantification of Western blot data is included in Supplementary Figure S1 B, C and D. Black arrows indicate the molecular weight of proteins.