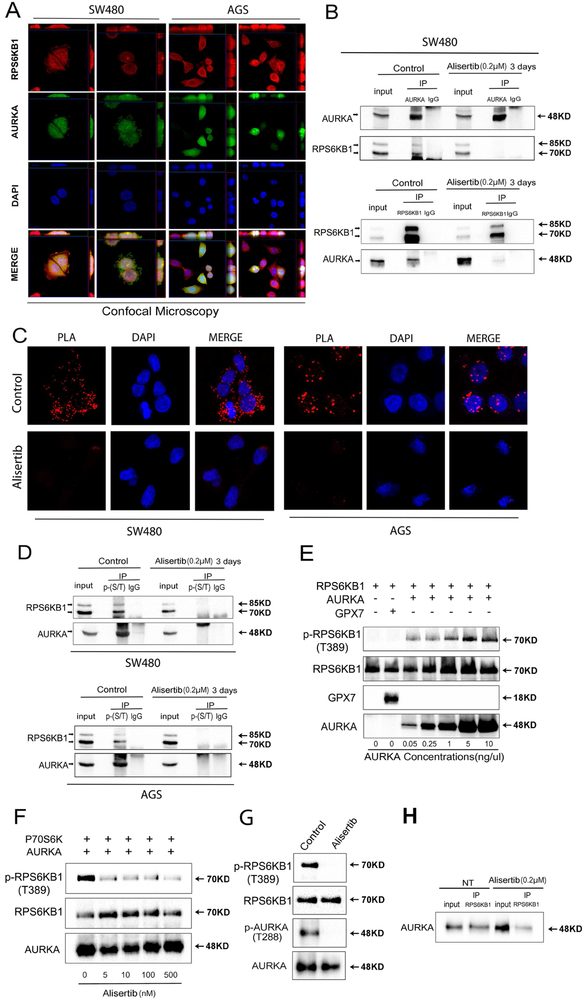
Figure 4. AURKA directly binds and phosphorylates RPS6KB1 at Thr-389.
A, Dual immunofluorescence showed co-localization (yellow) of AURKA (green) and RPS6KB1 (red) in SW480 and AGS cells. Z-stacking was displayed on top of each panel for X axis and on the right side of each panel for Y axis. Representative image is from one of three independent experiments. B, Immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis, following the treatment with or without alisertib for 3 days, indicates that AURKA directly binds to and phosphorylates RPS6KB1 (T389) protein. C, Proximity ligation assay (PLA) analysis indicates that AURKA co-localizes and interacts with RPS6KB1 in control groups (red dots, top row). Co-localization of AURKA and RPS6KB1 was reduced in alisertib treatment groups (bottom row). D, Western blot analysis of immunoprecipitation assay products, following pull-down of serine and threonine phosphorylated proteins, showed alisertib treatment downregulated phosphorylation of RPS6KB1 at threonine 389 in SW480 and AGS cells. E, Western blot analysis of in vitro kinase assay products by using increasing-concentrations of recombinant AURKA protein to react with 0.2 pg/pl recombinant RPS6KB1 proteins, or Glutathione peroxidase 7 protein (GPX7) (as a negative control). The data showed increased binding of AURKA with p-RPS6KB1 (T389). F, Western blot analysis of in vitro kinase assay products following increasing concentrations of alisertib. G, In vitro kinase assay for AURKA and RPS6KB1 with or without alisertib (0.5 μM) was performed followed by Western blotting for p-AURKA (T288), AURKA, p-RPS6KB1 (T389), and RPS6KB1. H, Western blot analysis following immunoprecipitation of the in vitro kinase assay products. The data indicate that AURKA directly binds to RPS6KB1.