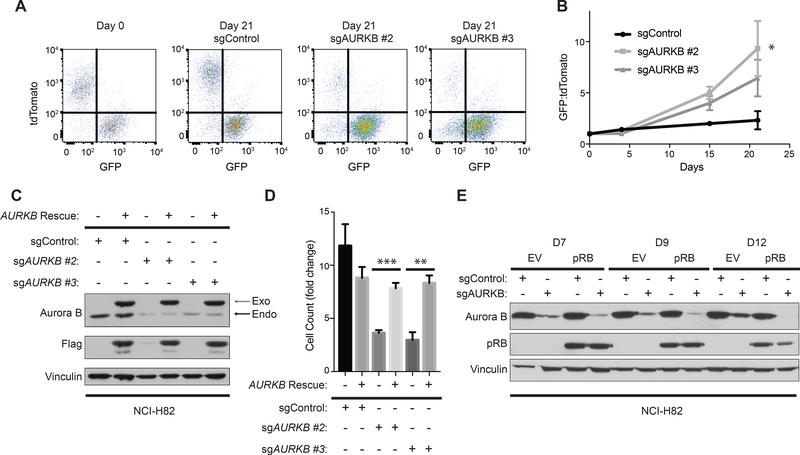
Figure 2: Genetic inactivation of AURKB is synthetic lethal with RB1 loss in NCI-H82 cells.
A, FACS analysis of NCI-H82 cells infected to produce both pRB and GFP (infected with pRB-IRES-GFP lentivirus) or to produce tdTomato (infected with EV-IRES-tdTomato lentivirus) after being mixed at a 1:1 ratio and infected with a lentivirus expressing Cas9 and the indicated sgRNA. B, Quantification of the GFP:tdTomato ratio at the indicated timepoints of cells treated as in A. n=5 biological replicates. *=p<0.05 of sgAURKB #2 at day 21 compared to sgControl. C, Immunoblot analysis, and D, cellular proliferation assays [based on cell count (fold change relative to day 0)] of NCI-H82 cells that were infected with a Dox-inducible sgRNA-resistant Aurora B kinase cDNA and superinfected with the indicated sgRNAs. The cells were selected in the presence of DOX (see Methods) to maintain expression of the sgRNA-resistant Aurora B Kinase and then grown in the presence or absence of DOX to either maintain or withdraw expression of exogenous Aurora B kinase for 5 days. n=4 biological replicates. **=p<0.01, ***=p<0.001. In C, gray arrow shows exogenous Aurora B kinase and black arrow shows endogenous Aurora B kinase. E, Immunoblot analysis of NCI-H82 cells expressing Cas9 that were superinfected with DOX-On pRB or DOX-On EV (see Supplementary Fig. S1A), grown in the presence of DOX, and then infected with a lentivirus expressing the indicated sgRNA. Cell extracts were harvested at the times indicated after introducing the sgRNAs.