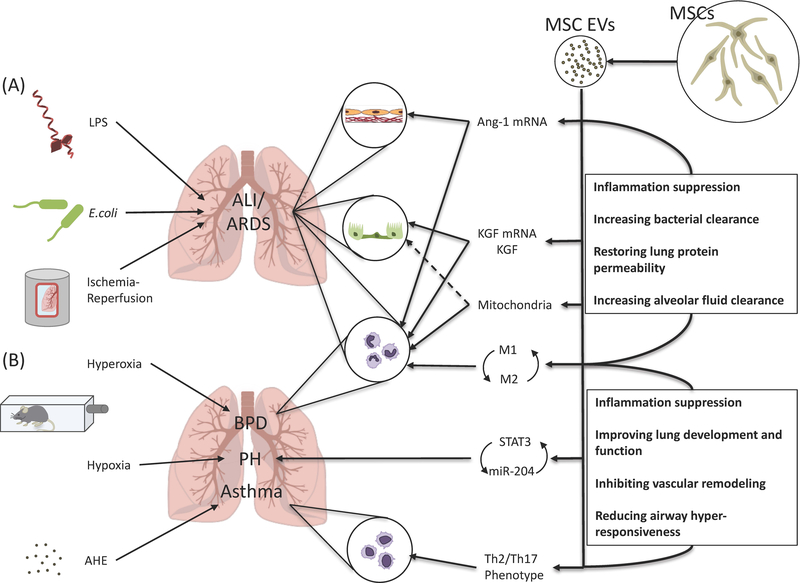
Figure. Therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells in acute lung injury.
(A) In ALI models with various etiologies including lipopolysaccharide, Escherichia coli bacteria, and ischemia-reperfusion injury, administration of MSC-derived EVs was associated with the transfer of Ang-11 and KGF mRNA and possibly mitochondria from the EVs to the alveolar epithelium and endothelium, contributing in preservation of alveolar-capillary permeability and improved alveolar fluid clearance. MSC-derived EVs also changed monocyte/macrophage towards an anti-inflammatory phenotype with increased phagocytic activity, which resulted in increased bacterial clearance. (B) In a model of hyperoxia-induced bronchopulmonary dysplasia, MSC-derived exosomes improved lung architecture and function through modulation of lung macrophage phenotype, suppressing the pro-inflammatory M1 and augmenting an anti-inflammatory M2-like state. In a model of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension, MSC-derived exosomes also prevented vascular remodeling by suppressing the hypoxic induction of STAT3 and up-regulated miR-204 levels, interfering with the STAT3-miR-204-STAT3 feed-forward loop. In a model of aspergillus hyphal extract-induced asthma, MSC-derived EVs mitigated Th2/Th17-mediated airway hyper-responsiveness by shifting the Th2/Th17 inflammatory response towards a counter-regulatory Th1 response. MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; EV, extracellular vesicle; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; E. coli, Escherichia coli; ALI, acute lung injury; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; Ang-1, angiopoietin-1; KGF, keratinocyte growth factor; BPD, bronchopulmonary dysplasia; PH, pulmonary hypertension; STAT3, signal transducer and activator transcription 3; AHE, aspergillus hyphal extract.