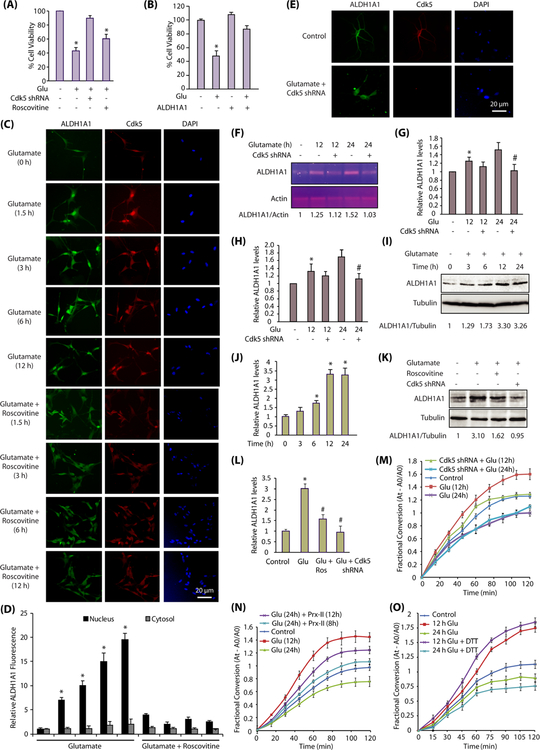
Fig. 7.
Cdk5-ALDH1A1 signaling in primary neurons. a Inhibition and ablation of Cdk5 inhibits neurotoxicity in primary cortical neurons. Cdk5-shRNA-infected primary neurons (30 h) were treated with glutamate (24 h). Cell viability was tested by an MTT assay. *p < 0.05, compared with untreated neurons. b Overexpression of ALDH1A1 prevents neurotoxicity in primary cortical neurons. ALDH1A1 overexpressed primary neurons (30 h) were treated with glutamate (24 h). Cell viability was tested by MTT assay. *p < 0.05, compared with untreated neurons. c Glutamate exposure triggers nuclear translocation of ALDH1A1 in a Cdk5-dependent manner. Primary cortical neurons were treated with glutamate (100 μM) for 12 h in the presence or absence of roscovitine (10 μM), followed by immunostaining with Cdk5 and ALDH1A1 antibodies. d Quantification of the subcellular localization of ALDH1A1 in the cell nucleus versus the cytoplasm. The graphs show the mean ± SEM of the relative fluorescence intensity with respect to control cells. *p < 0.05 versus nucleus fraction control analyzed by two-way analysis of variance. e Cdk5 depletion inhibits nuclear translocation of ALDH1A1. Primary cortical neurons were treated with glutamate (100 μM) for 12 h in the presence or absence of Cdk5 shRNA, followed by immunostaining with Cdk5 and ALDH1A1 antibodies. f Primary cortical neurons were treated with glutamate for 12 and 24 h, in the presence and absence of Cdk5 shRNA, and then, the total levels of ALDH1A1 mRNA were analyzed using semi-quantitative RT-PCR. g ALDH1A1 mRNA levels in primary cortical neurons in response to glutamate treatment with or without Cdk5 shRNA. Graphical results are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, compared with untreated primary cortical neurons.#p < 0.05, compared with only glutamate-treated neurons. h Primary cortical neurons were treated similarly as described for f, g, and total mRNA levels of ALDH1A1 were detected by real-time qPCR. Expression levels are normalized to the expression of actin. Results are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, compared with untreated neurons.#p < 0.05, compared with only glutamate-treated neurons. i Glutamate treatment increases ALDH1A1 protein levels in primary cortical neurons in a time-dependent manner. Primary cortical neurons were treated with glutamate for 0–24 h and the total levels of ALDH1A1 analyzed. j Average relative ratios of ALDH1A1 band intensities to alpha-tubulin band intensities upon glutamate treatment as obtained from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, compared with untreated primary neurons. k Glutamate treatment increases ALDH1A1 protein levels in primary cortical neurons in a Cdk5-dependent manner. ALDH1A1 levels were analyzed upon glutamate (12 h), roscovitine, and Cdk5 shRNA treatments. l ALDH1A1 protein levels in primary cortical neurons in response to glutamate treatment with or without roscovitine and Cdk5 shRNA. Graphical results are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, compared with untreated primary neurons, and#p < 0.05, compared with only glutamate-treated primary neurons. m ALDH1A1 enzyme activity in primary cortical neurons in response to glutamate treatment with or without Cdk5 shRNA. n Removal of oxidative stress restores ALDH1A1 activity to a significant extent. Primary cortical neurons were either treated with glutamate for 12 and 24 h or were pretreated with glutamate for 12 and 16 h, followed by subsequent treatment with 200-nM TAT-fused peroxiredoxin-II-T89A for the next 12 and 8 h, respectively. TAT-fused peroxiredoxin-II-T89A protein was purified fresh and added every 4 h. TAT-fusion red fluorescent protein (TAT-RFP) was used as a control. ALDH1A1 immune complex was isolated, and its dehydrogenase activity was determined as described in the “Materials and Methods” section. o DTT treatment is beneficial for ALDH1A1 enzymatic activity initially. Primary cortical neuron cells were treated with glutamate for 12 and 24 h. ALDH1A1 was immunoprecipitated using ALDH1A1 antibody, and enzyme activity was performed with or without 10 mM DTT in reaction buffers as described in the “Materials and Methods” section