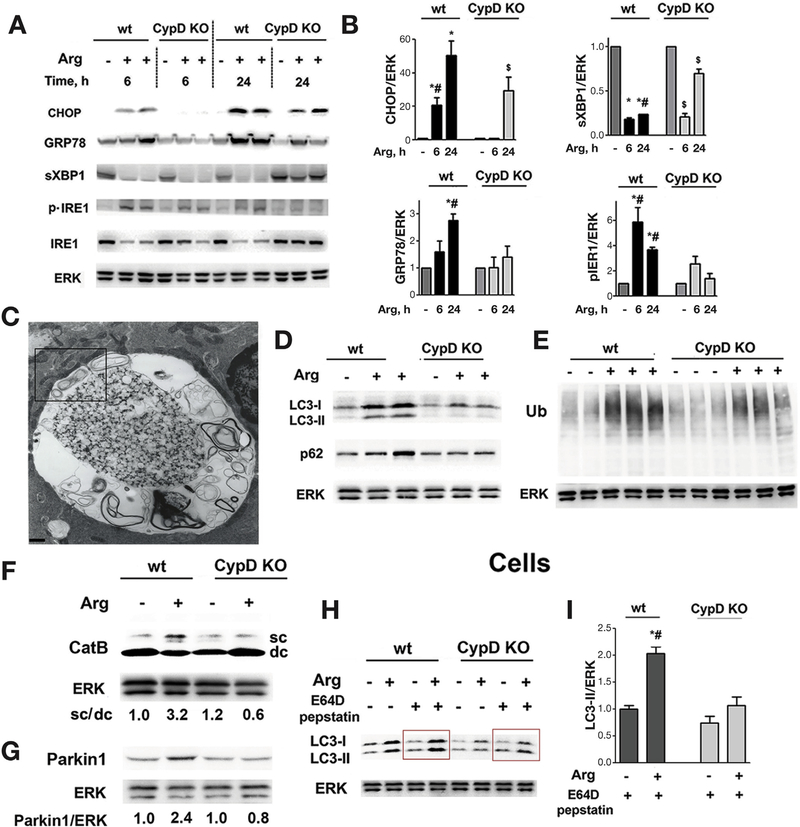
Figure 5.
Cyclophilin D genetic ablation alleviates ER stress and normalizes autophagy in Arg-AP. Mice were subjected to Arg-AP and killed at indicated times (A,B) or at 24 hours (C-I). Markers/mediators of (A,B) ER stress, (D-F) autophagic/lysosomal pathways, and (G) mitophagy were analyzed in pancreatic tissue by IB. Ub, ubiquitin; CatB, cathepsin B. The IB in (F) shows the intermediate/single-chain (sc) CatB form and the heavy chain of mature/double-chain (dc) form. (C). EM showing abnormally large autolysosome with poorly degraded material in pancreas of Arg-AP mouse. The boxed area is enlarged in Supplementary Figure 10. Scale bar: 1.7 μm. (H,I). Pancreatic acinar cells were isolated from mice of indicated groups, incubated for 2 hours in the presence or absence of lysosomal protease inhibitors, E64D + pepstatin A (20 μmol/L each), and LC3-I/II levels measured by IB. In (B) and (I), densitometric band intensities for specified proteins were normalized to that of ERK in the same sample, and the mean ratios further normalized to that in wt control group. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < .05 vs wt saline-treated mice; #P < .05 vs same treatment in CypD KO mice; $P < .05 vs saline-treated CypD KO mice.