FIGURE 1.
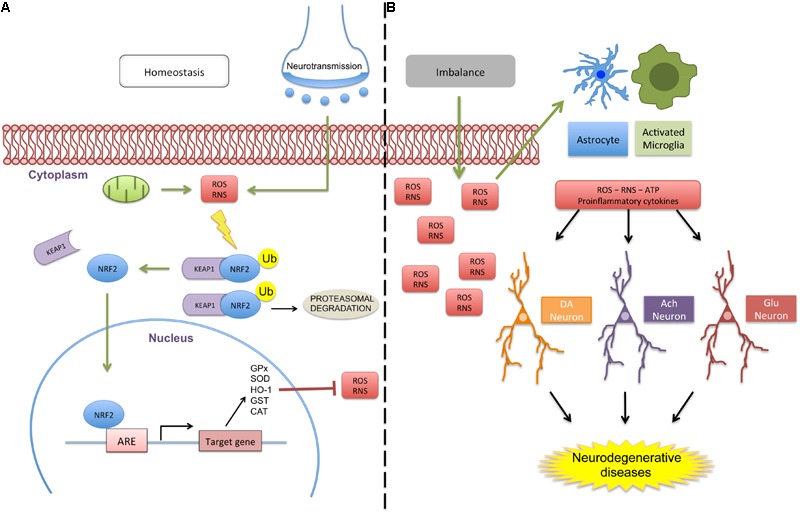
Schematic representation of Nrf2 signaling in homeostasis and a deregulated environment. (A) Oxidative molecules (e.g., ROS and RNS) produced by cellular respiration or neurotransmission activate the protective antioxidant pathway by dissociation of the Nrf2/KEAP1 complex. When dissociated from the cytosolic protein KEAP1, Nrf2 translocates to the cell nucleus, triggering the expression of several homeostatic genes with the ARE sequence in their promoters, including GPx, SOD, HO-1, GST, and CAT. When inactivated, Nrf2 is sequestered by KEAP1 and targeted for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. (B) Altered homeostasis promotes excessive ROS/RNS production that can activate glial cells (astrocytes and microglia) that release proinflammatory and danger molecules patterns, which disrupts neuronal communication and the nature of glial activities. Green arrows represent activation and truncated red lines, inhibition (abbreviations: ACh, acetylcoline; DA, dopamine; CAT, catalase; Glu, glutamate; GPx, Glutathione Peroxidase; GST, glutathione S-transferase; HO-1, heme oxigenase 1; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; Ub, ubiquitin; ATP, adenosine triphosphate).
