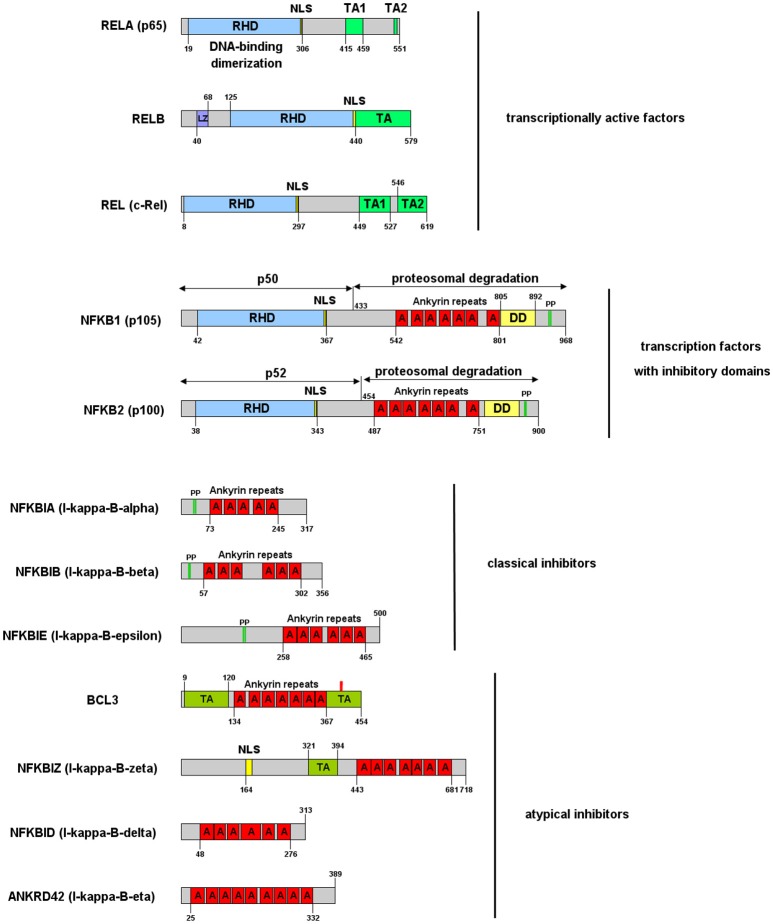
Figure 1.
NF-κB and IκB family of proteins and their functional domains. The proteins are designated by their gene symbols with frequently used aliases in brackets. RHD, Rel-homology domain, responsible for DNA binding and dimerization; TA, transactivation domain, responsible for binding of the transcriptional machinery and RNA-polymerase; LZ, leucine zipper; NLS, nuclear localization domain; A, ankyrin repeat; DD, death domain; PP, double-phosphorylation by IκB kinases triggering ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation or processing (in case of NFKB1 and NFKB2). The numbers specify the amino acid borders of domains for human isoforms. Atypical inhibitors are described in more detail in Pettersen et al. (13).