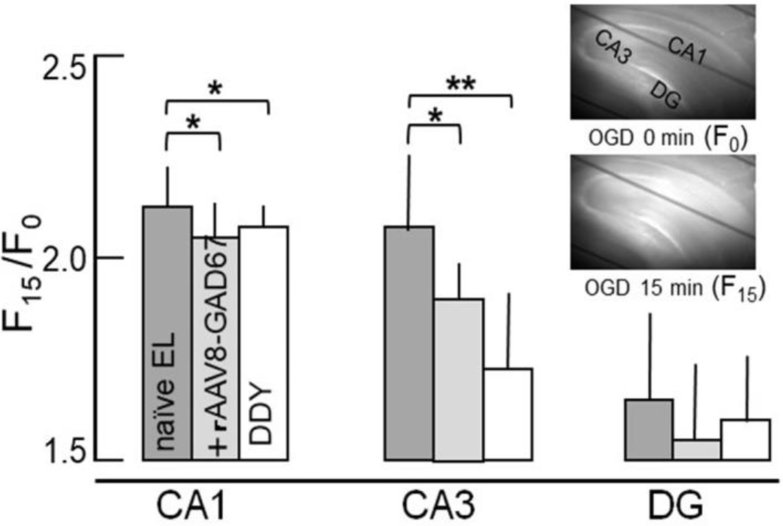
Figure 4.
Fluorescence Quantitation in DDY, Naive EL, and rAAV8-GAD67-Treated EL Mice under Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation Exposure
The changes in [Ca2+]i concentrations in the hippocampal slices after OGD exposure using rhod2-AM. Changing the incubation medium from normal to OGD caused, an abrupt increase in [Ca2+]i in the CA1 subfield at 10 min after switching. The sequential changes in [Ca2+]i following OGD in hippocampal slices from DDY, naive EL, and rAAV8-treated EL mice were examined using rhod2-AM. Regional differences in fluorescence signals increased after 15 min of exposure to ODG (inset panels; OGD 0 min and OGD 15 min). The hippocampal CA1, CA3, and DG regions were selected, and fluorescence signals were measured with an image processor. The baseline fluorescence (F0) was normalized to 1.0. Values represent mean ± SD. Fluorescence intensities at time 15 (F15/F0, average ± SD) were 2.23 ± 0.12 (naive EL mice, n = 8), 2.09 ± 0.11 (rAAV8-GAD67-treated EL mice, n = 5), and 2.11 ± 0.05 (DDY mice, n = 8) in CA1; 2.11 ± 0.21 (naive EL mice), 1.83 ± 0.11 (rAAV8-GAD67-treated EL mice), and 1.71 ± 0.21 (DDY mice) in CA3; and 1.61 ± 0.26 (naive EL mice), 1.56 ± 0.21 (rAAV8-GAD67-treated EL mice), 1.58 ± 0.19 (DDY mice) in dentate gyrus (DG). The results were analyzed by Tukey-Kramer. *Risk rate is less than 5%. **Risk rate is less than 1%. Hippocampal slices from DDY and rAAV8-treated mice showed significantly lower [Ca2+]i than those of naive EL mice after OGD exposure.