Table 2.
E3 protein ligand, structure of the linker and POI ligand with a description of the properties for kinases.
| Table entry | E3 protein (ligand) | Linker | POI ligand | POI | Potency/efficacy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | VHL (9) | 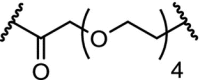 |
 |
RIPK2 | 50% RIPK2 degradation at 1.4 nM after 1 hour. Dmax of >95% at 10 nM | Bondeson [7] |
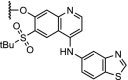
| 2. | VHL and CRBN (9 and pomalidomide) | 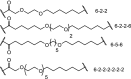 |
imatinib, bosutinib, and dasatinib | Tyrosine kinase: BCR-ABL | >60% degradation at 1 μM for the dasatinib-CRBN PROTAC. No degradation for the VHL-based PROTACs. | Lai [48] |
| 3. | CRBN (thalidomide) | 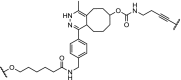 |
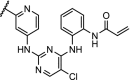 |
ERK1 and ERK2 | In-cell click reaction where ERK1/2 degradation is observed partially after 4 h and is complete after 16 h at 10 μM | Lebraud [84] |
| 4. | CRBN (thalidomide) | n-pentyl | 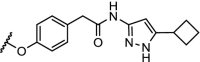 |
CDK9 | Selective for CDK9. 56% degradation of CDK9 at 10 μM. | Robb [95] |
| 5. | VHL (9) | Diethylene glycol | Lapatinib, gefitinib, afatinib | RTKs: EGFR, HER2 and c-MET | Efficient degradation of transmembrane RTKs with superior outcome over RTK inhibitors. | Burslem [98] |
| 6. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 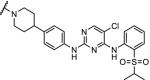 |
Multi- kinase degrader | Quantitative proteomics showed degradation of 28 kinases including BTK, FLT3 and nine members of the CDK family | Huang [91] | |
| 7. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 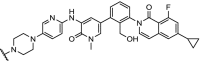 |
BTK | Most efficient degradation at 100 nM concentration. In addition, a bosutinib-based degrader was reported | Huang [91] | |
| 8. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 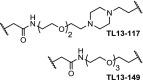 |
 |
FLT3 | Concentrations between 10 and 100 nM resulted in the most efficient degradation of FLT3. | Huang [91] |
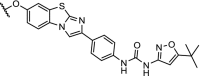
| 9. | VHL (9) | 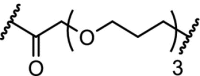 |
TBK1 | Extensive linker optimization. DC50: 12 nM with Dmax: 96%. | Crew [99] | |
| 10. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 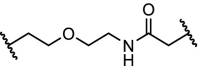 |
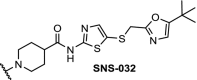 |
CDK9 | The multi target inhibitor SNS-032 became selective for CDK9 as PROTAC with near complete degradation at <250 nM concentration | Olson [96] |
| 11. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | Six different linkers were used. The best results were obtained with: 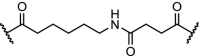
|
 |
PI3K | IC50 for PI3K: 24 nM. time-/concentration-dependent degradation PI3K protein observed. Inhibition of HepG2 cell growth via autophagy | Li [100] |
| 12. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 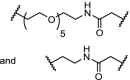 |
 |
ALK | DC50: 3 and 11 nM respectively after 16 h in SU-DHL-1 cells. Potent inhibition of proliferation of SU-DHL-1 cells. Both linkers effective | Zhang [101] |
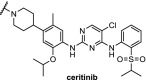
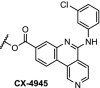
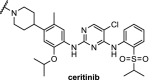
| 13. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | Ceritinib and TAE684[108] | ALK | DC50 of 10 nM for both PROTACs in H3122 cells. ABCB1 was responsible for efflux. | Powel [102] | |
| 14. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 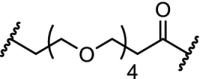 |
 |
CDK8 | CDK8 IC50: 159 nM. Significant degradation of CDK8 in Jurkat cells after treatment for 24 hr at 1 μM concentration | Hatcher [103] |
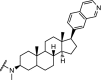
| 15. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 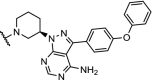 |
BTK | Efficiently degradation of BTK-WT. Induced degradation of ibrutinib-resistant BTK-C481S (50% degradation efficiency at 30 nM) | Sun [104] | |
| 16. | CRBN (5) | 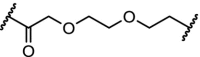 |
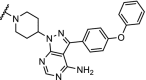 |
BTK | >99% degradation of mutated C481S and wildtype BTK at nM concentrations. Enhanced selectivity over ibrutinib | Buhimschi [37] |
| 17. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 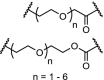 |
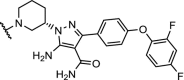 |
BTK | For n = 4 – 6 DC50’s between 1 and 40 nM. n = 1 – 3 are ineffective in degradation of BTK. | Zorba [41] |
| 18. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 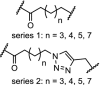 |
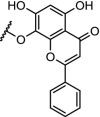 |
CDK9 | Serie 2 (n = 5) showed the most efficient CDK9 degradation in the concentration range of 1 to 30 μM. Inhibition of MCF cell proliferation with an IC50 of 17 μM | Bian [97] |
| 19. | CRBN (pomalidomide) | 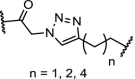 |
 |
CK2 | Most promising results for n = 2. Degradation of CK2 in a dose and time-dependent manner resulting in downstream reduced phosphorylation of Akt | Chen [107] |
| 20. | VHL (9) | 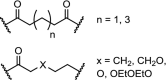 |
 |
ALK | n = 1 displayed the best properties. 90% ALK degradation at 1 μM after 16 h. in SU-DHL-1 cells. Excellent efficacy in tumor xenograft mice. | Kang [100] |
The structure of the CRBN ligands and the VHL ligand (9) are shown in Fig. 2.
