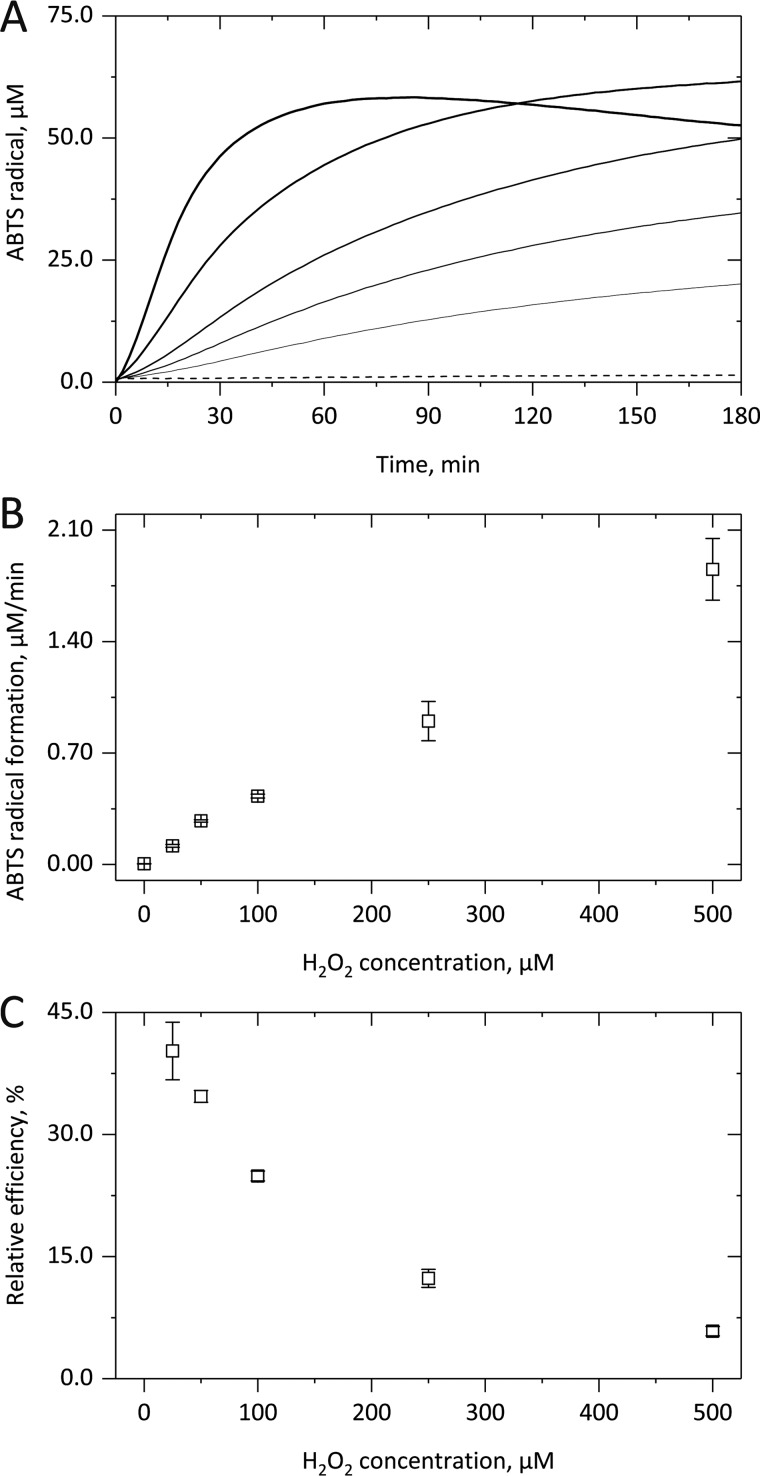
Figure 1.
H2O2-dependent peroxidase activity of cytochrome c. After adding up to 500 μm H2O2 to 5 μm cyt c, the formation of ABTS+• from 1 mm ABTS in 10 mm PB, pH 7.4, was followed for up to 3 h at 37 °C by monitoring the absorbance increase at 734 nm. The kinetic curves in A illustrate that in the presence of increasing H2O2 concentrations (straight lines; 25, 50, 100, 250 and 500 μm) a shorter lag phase, a higher linear ABTS+• formation rate, and a quicker deactivation of the cyt c–based peroxidase activity were observed. In B, the linear increase of the cyt c–derived enzymatic activity with H2O2 concentration is shown. In C, the coinciding exponential decrease in the relative efficiency of the cyt c-derived peroxidase activity is illustrated. In A, averaged kinetic curves from three independent experiments are shown; in B and C, the corresponding mean (points) and S.D. (error bars) values are given.