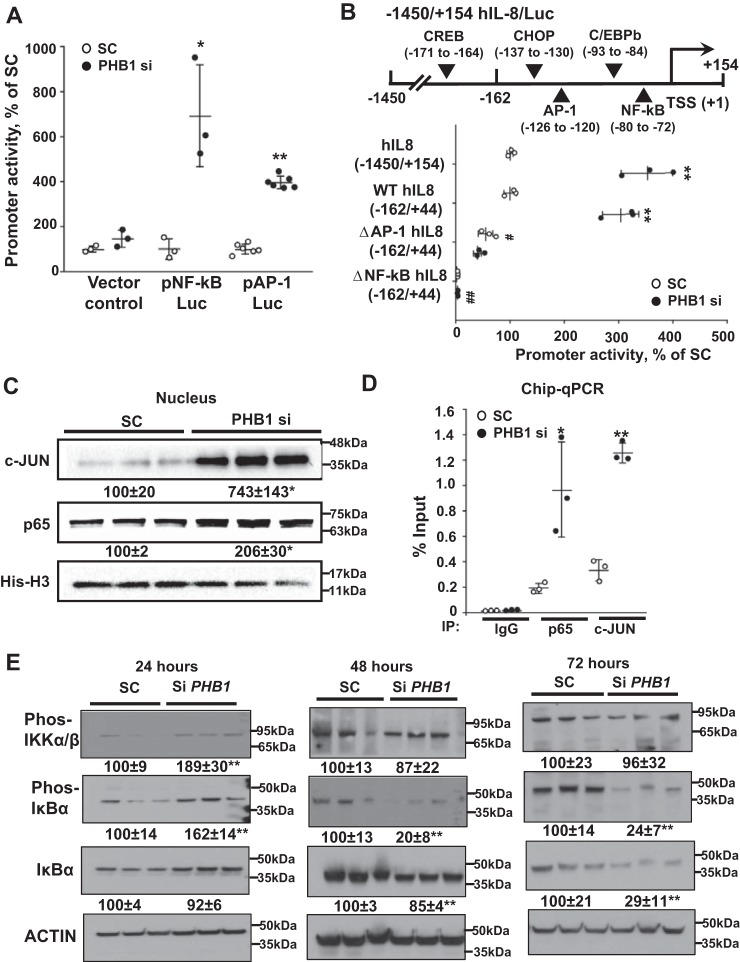
Figure 5.
PHB1 silencing-induced IL-8 promoter activity requires NF-κB and AP-1. A, promoter activity of NF-κB- and AP-1-driven luciferase reporter constructs after PHB1 knockdown. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E. of the mean from at least three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus SC. B, effects of NF-κB and AP-1 sites mutations on PHB1 silencing-induced transcription from the IL-8 promoter. HepG2 cells were transfected with PHB1 siRNA, and effects on IL-8 promoter (1450/+154) activity or reporter activities driven by the human IL-8 promoter (162/+44) WT or mutated in the AP-1 or NF-κB elements were measured. **, p < 0.01 versus respective controls; ##, p < 0.01 versus SC of the WT IL-8 promoter. C, Western blots of c-Jun and p65 in nuclear extracts from PHB1 knockdown HepG2 cells. All densitometric values were normalized to histone H3. D, effects of PHB1 knockdown on p65 and c-Jun binding to regions of the IL-8 promoter, measured by ChIP quantitative PCR. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E. from at least three independent experiments. **, p < 0.01 versus respective controls. SC, scramble siRNA; PHB1 si, PHB1 siRNA. E, Western blots of the NF-κB signaling pathway upon PHB1 knockdown. PHB1 was knocked down between 24 and 72 h in HepG2 cells, and phospho-IKKα/β (Ser-176/180), phospho-IκBα (Ser-32), and IκBα were blotted. All densitometric values were normalized to actin. **, p < 0.01 versus the respective SC control.