Figure 1.
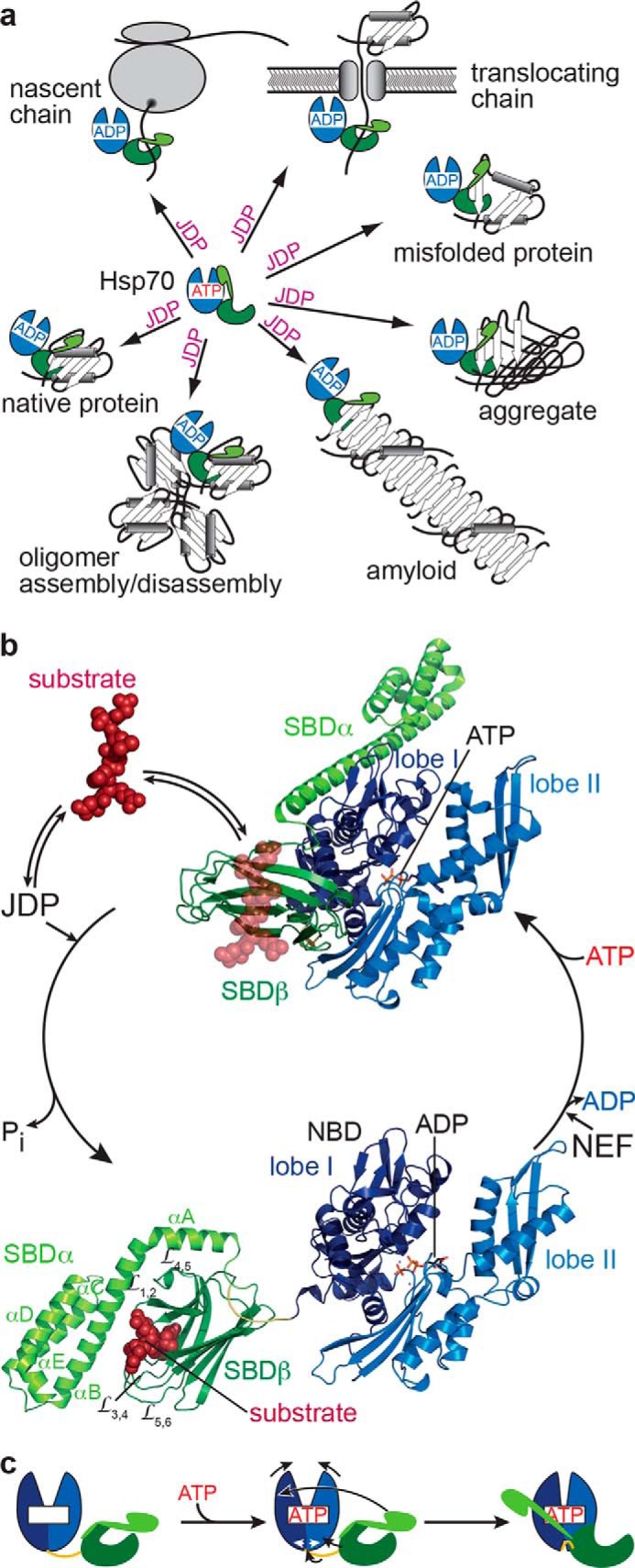
Hsp70 functions and ATPase cycle. a, JDPs target Hsp70s to a diverse set of substrates, including nascent polypeptide chains at the ribosome or translocation pore, to misfolded, aggregated, or amyloidic proteins, to oligomeric protein complexes, and to certain native proteins. b, structures of E. coli DnaK in the ATP-bound open conformation (PDB code 4B9Q, (16)) and the ADP-bound closed conformation (PDB code 2KHO (13)) with NBD lobe I in dark blue, lobe II in light blue, the conserved interdomain linker in yellow, SBDβ in dark green, and SBDα in light green. Substrates (dark red) targeted by JDPs bind with high association rates to the open conformation of Hsp70·ATP (indicated as transparent peptide from the aligned 1DKX structure (10)) and in synergism with the JDP trigger ATP hydrolysis and transition to the ADP-bound closed high-affinity state. NEFs accelerate ADP release, and rebinding of ATP converts Hsp70 back to the low-affinity ATP-bound state with subsequent substrate release. c, schematic illustrating ATP-induced conformational changes in Hsp70s; colors as in b.
