Figure 4.
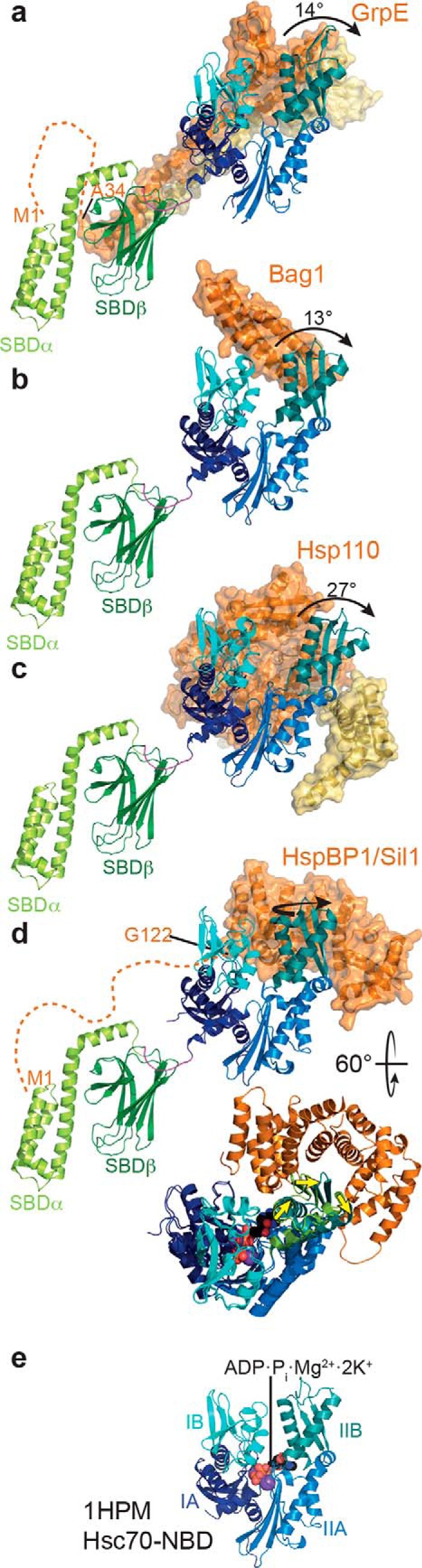
Mode of action of NEFs. Cartoon and surface representations of crystal structures of different NEFs (orange and yellow) in complex with an Hsp70 NBD (IA, dark blue; IB, cyan; IIA, light blue; IIB, dark teal), overlaid onto the full-length solution structure of DnaK (PDB code 2KHO (13), only SBD shown) to illustrate the position of the SBD. From top to bottom: E. coli GrpE in complex with E. coli DnaK–NBD (a, PDB code 1DKG (91)); Bag-domain of human Bag1 in complex with the NBD of bovine Hsc70 (b, PDB code 1HX1 (124)); yeast Sse1 in complex with the NBD of bovine Hsc70 (c, PDB code 3D2E (125)); yeast Sil1 in complex with the NBD of yeast Kar2 (d, PDB code 3QML (126)); yeast Sil1 in complex with the NBD of yeast Kar2 overlaid to bovine Hsc70 and rotated as indicated (yellow arrow indicates the displacement of subdomain IIB); e, NBD of bovine Hsc70 in complex with ADP, phosphate, Mg2+, and two K+ ions (PDB code 1HPM (68)). The NBDs of all structures are aligned to subdomains IA, IB, and IIA of the NBD of bovine Hsc70. Dashed lines at the N termini of GrpE and Sil1 indicate the unstructured regions not present in the crystal structure and proposed to bind into the substrate-binding pocket of Hsp70 (115, 116). The N-terminal methionine (M1) and the first residue in the structure are indicated.
