Table 1. Variation of the reaction parameters for the Ni-catalysed reductive arylalkylation reaction a .
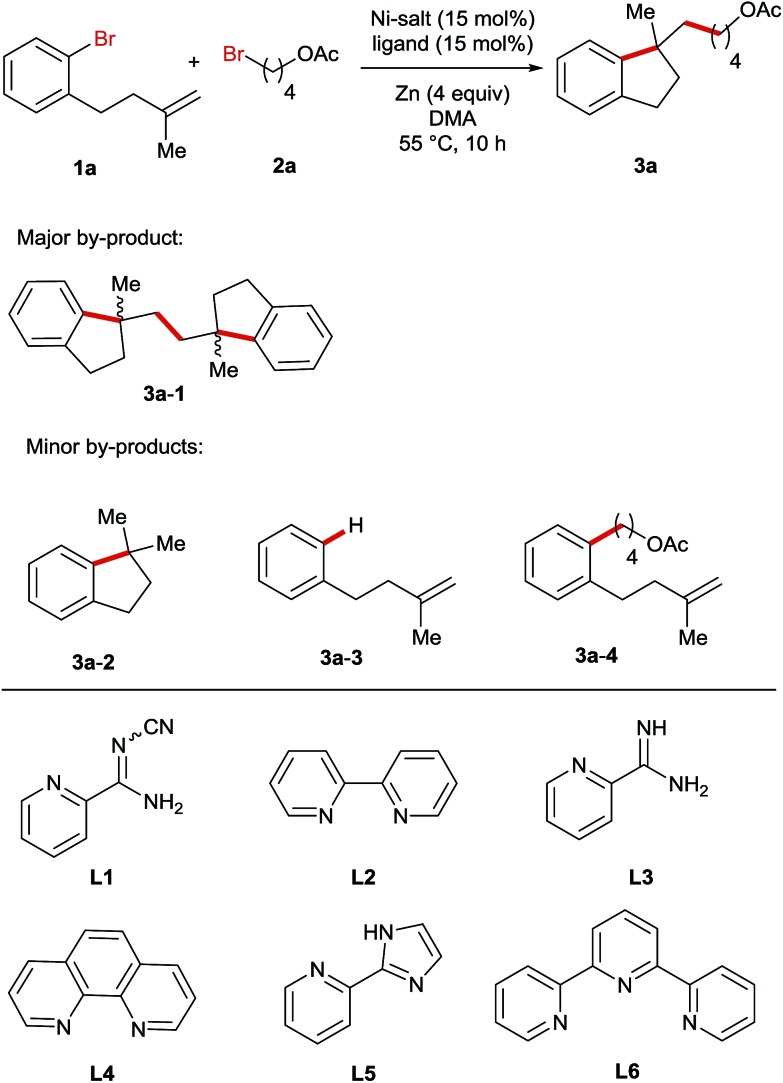
| |||
| Entry | Variation from the optimum conditions | Yield 3a b (%) | Yield: 3a-1 b (%) |
| 1 | None | 69 (67 c ) | 9 |
| 2 | Iodo-analogue of 1a used | 32 | 19 (8 d ) |
| 3 | Iodo-analogue of 2a used | 10 | 18 (31 d ) |
| 4 | Both iodo-analogues of 1a and 2a used | 17 | 10 (30 d ) |
| 5 | L2 instead of L1 | 30 | 49 |
| 6 | L3 instead of L1 | 45 | 2 |
| 7 | L4 instead of L1 | 54 | 13 |
| 8 | L5 instead of L1 | 32 | 50 |
| 9 | L6 instead of L1 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | NiI2 instead of NiBr2 | 61 | 8 |
| 11 | Ni(OTf)2 instead of NiBr2 | 32 | 4 |
| 12 | NiBr2·glyme instead of NiBr2 | 63 | 8 |
| 13 | Ni(COD)2 instead of NiBr2 | 63 | 7 |
| 14 | DMF instead of DMA | 43 | 3 |
| 15 | NMP | 68 | 8 |
| 16 | THF instead of DMA | 0 | 0 |
| 17 | MeCN instead of DMA | 0 | 0 |
| 18 | Mn instead of Zn | 51 | 17 |
| 19 | 75 °C instead of 55 °C | 62 | 8 |
| 20 | 35 °C instead of 55 °C | 27 | 2 |
| 21 | 1.2 equiv. 2a used | 50 | 13 |
| 22 | 10 mol% NiBr2 used | 63 | 13 |
| 23 | 2 equiv. Zn used | 50 | 7 |
aUnless otherwise specified, reactions were performed on a 0.2 mmol scale of aryl bromide 1a with 2 equiv. bromobutyl acetate (2a), 15 mol% NiBr2, 15 mol% ligand L1 and 4 equiv. Zn as the reductant in 0.5 mL DMA at 55 °C for 10 h.
bGC-yields using n-dodecane as an internal standard.
cYield of the isolated product.
dYield of 3a-2.
