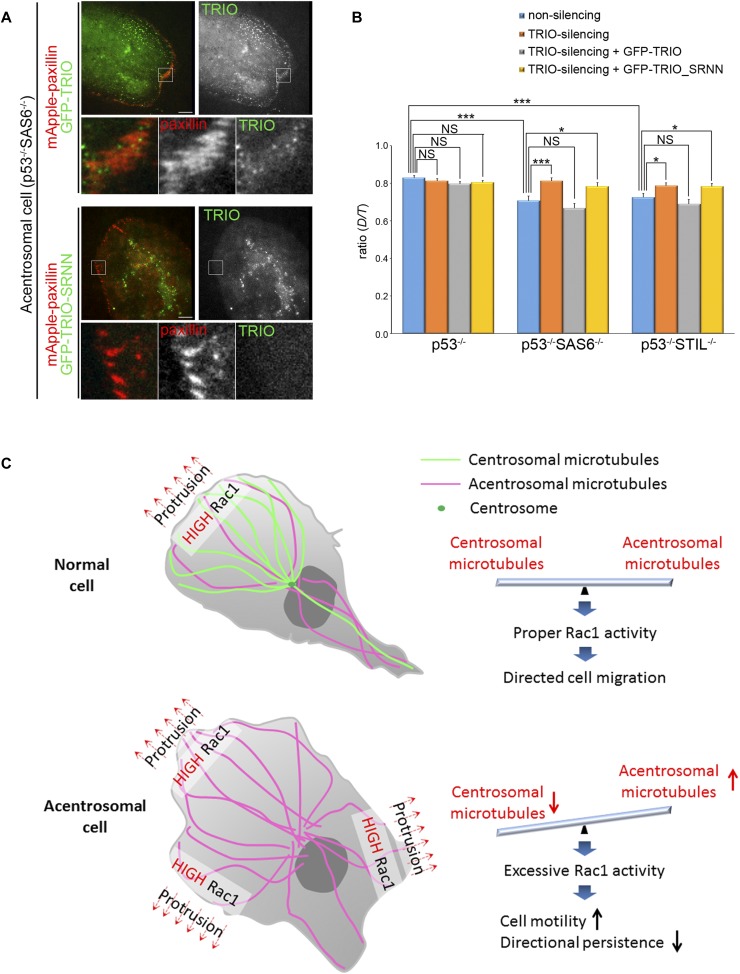
Figure 7. Effects of TRIO on cell migration.
(A) TIRF microscopy images of RPEp53−/−SAS6−/− cells expressing mApple-paxillin (red) with either GFP-TRIO (green) or GFP-TRIO-SRNN (green). Scale bar, 10 μm. The 9.6-μm × 9.6-μm areas indicated in the upper images are magnified in the bottom three images. (B) Directional persistence of RPEp53−/−, RPEp53−/−SAS6−/−, and RPEp53−/−STIL−/−cells expressing non-silencing shRNA or TRIO-silencing shRNA alone or together with GFP-TRIO or GFP-TRIO-SRNN. Data are mean ± SEM (non-silencing RPEp53−/−, n = 57 cells; non-silencing RPEp53−/−SAS6−/−, n = 55 cells; non-silencing RPEp53−/−STIL−/−, n = 51 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/−, n = 61 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/−SAS6−/−, n = 49 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/−STIL−/−, n = 61 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/− cells expressing GFP-TRIO, n = 74 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/−SAS6−/− cells expressing GFP-TRIO, n = 60 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/−STIL−/− cells expressing GFP-TRIO, n = 54 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/− cells expressing GFP-TRIO-SRNN, n = 84 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/−SAS6−/− cells expressing GFP-TRIO-SRNN, n = 60 cells; TRIO-silencing RPEp53−/−STIL−/− cells expressing GFP-TRIO-SRNN, n = 53 cells). *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; NS, no significance. (C) Model showing the balance between centrosomal and acentrosomal microtubules during the control of Rac1 activation, FA dynamics, and directed cell migration. The centrosome acts as a controller and balances the formation of centrosomal and acentrosomal microtubules, which in turn restricts the random Rac1 activation caused by acentrosomal microtubules and activates Rac1 locally at cell front to induce membrane protrusion during directed cell migration. Interference with formation of the centrosome increases acentrosomal microtubules assembly, which results in the transportation of more TRIO protein, which in turn increases the excessive and random activation of Rac1. This then increases lamellipodia formation, leading to the loss of cell polarity and a negative impact on directed cell migration.