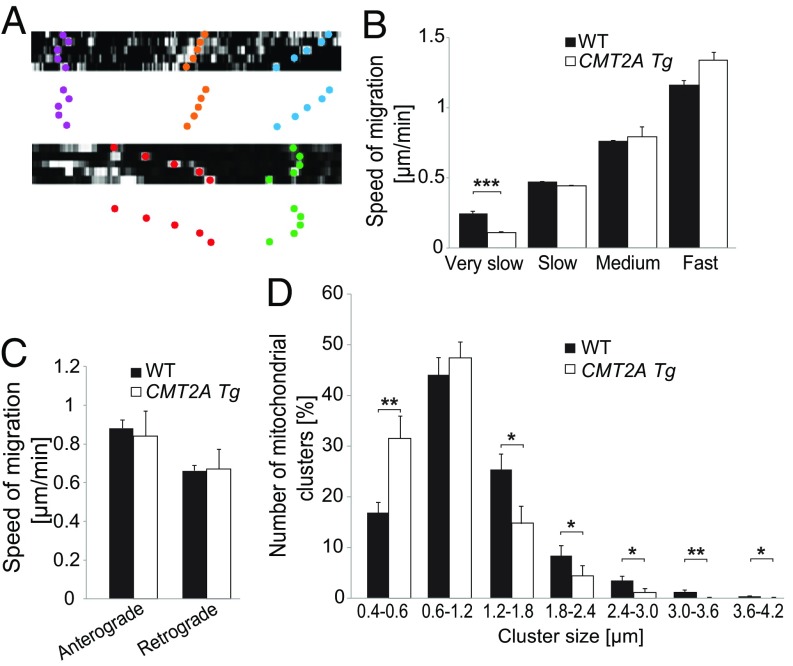
Fig. 6.
MFN2R94Q impairs mitochondrial transport and leads to overabundance of small mitochondria clusters in vivo. (A) Examples of kymographs used to determine mitochondrial velocity in sciatic nerve axons of 1-mo-old animals. Colored dots represent different types of mitochondrial movements. (B) mitochondria are classified according to very slow (<0.3 µm/min), slow (>0.3 and <0.6 µm/min), medium (>0.6 and <0.9 µm/min), and fast (>0.9 µm/min) transport velocities. Statistical analysis: two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. (C) Mitochondrial anterograde and retrograde transport velocities were evaluated in the sciatic nerve of WT (n = 74 mitochondria from seven mice) and CMT2A Tg (n = 29 mitochondria from six mice) mice. (D) Number of mitochondrial clusters according to cluster size in axons of WT (n = 23 axons from 10 mice) and CMT2A Tg (n = 16 axons from six mice) mice. Statistical analysis: two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.