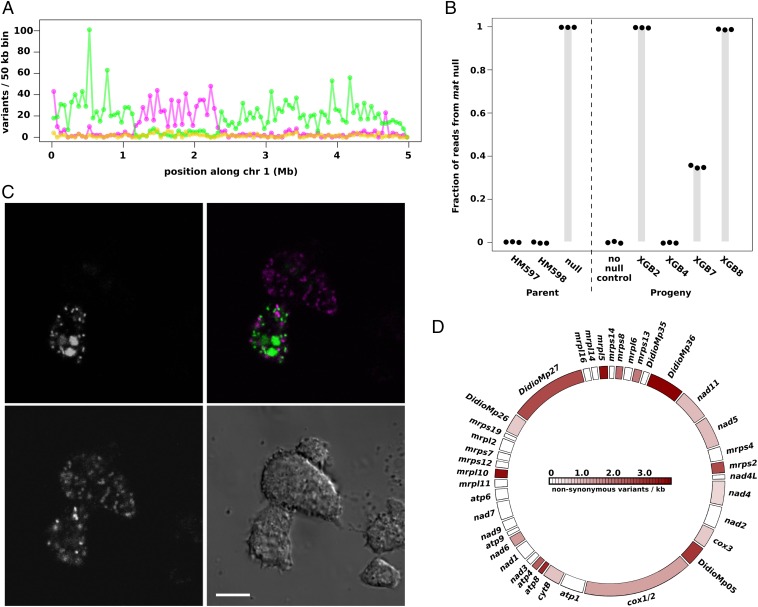
Fig. 4.
Lateral transmission of mitochondria in the Dictyostelium sexual cycle. (A) We have so far found no evidence for transmission of nuclear DNA from the mutant parent in a three-way cross between HM597, HM598, and the matA null strain HM1524; shown here is one representative chromosome from one progeny clone, XGB8. Variants specific to HM597 are shown in magenta, HM598 variants are in green, HM1524 (AX2) variants are in gold; all putative HM1524 variants appear to be false positives. (B) In contrast, lateral transfer of mitochondrial DNA clearly occurred in three of four sequenced progeny. Sequence reads specific to the matA null strain were counted at three positions along the mitochondrial genome for the three parent strains and one two-way progeny (“no null control”, XGB1), as well as the four three-way progeny. In the three progeny with lateral transmission of mtDNA, all other variants along the mitochondrial chromosome also showed similar contribution from the matA null. (C) Three-way fusions were directly observed between an HM598 line expressing GFP-tagged histone 2B (green, Upper Left), a AX2 line expressing GFP targeted to the mitochondrial matrix with the TopA N-terminal targeting motif (green, Upper Left), and an HM1558 line expressing RFP anchored on the mitochondrial outer membrane using the GemA C-terminal targeting motif (magenta, Lower Left). (Lower Right) A DIC image is shown. Mitochondria were mixed in the syncytial cytoplasm and were not observed to undergo fusion. (Scale bar, 10 µm.) (D) The D. discoideum mitochondrial genome is unevenly polymorphic: the density of nonsynonymous polymorphisms in protein coding genes across strains used in this study is shown (homing endonuclease genes are omitted). For comparison, the greenbeard genes tgrB1 and tgrC1 each have more than 40 polymorphisms per kilobase (31). atp4 is within the top percentile of polymorphic genes in D. discoideum according to this dataset; this gene, along with atp8, was found to have the highest dN/dS ratios in a comparison of mitochondrial genes in several social amoeba species (45).