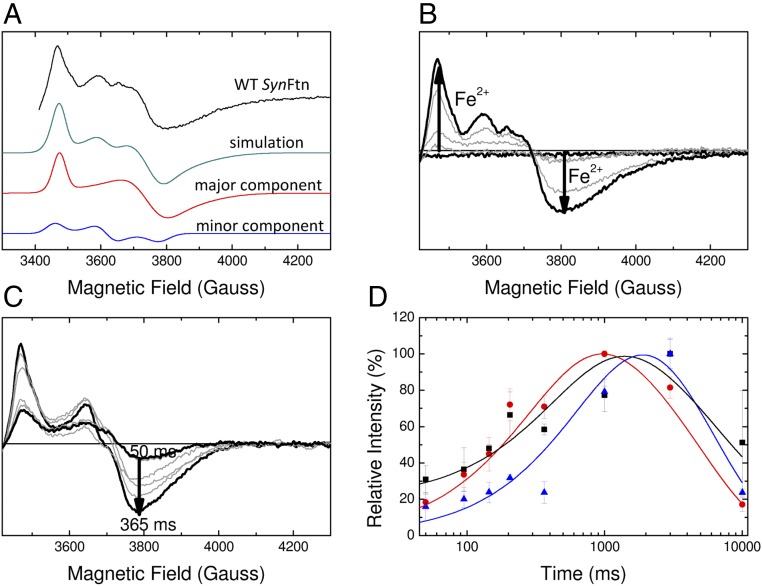
Fig. 3.
EPR monitored iron–O2 reactivity of SynFtn. (A) The EPR signal attributed to a mixed-valent (Fe2+/Fe3+) form of the ferroxidase center (MVFC) in SynFtn frozen 12 s after initiating iron oxidation (iron added at 80 Fe2+/Ftn) and its modeling as a sum of two signals simulated with the parameters listed in Table 1. Experimental data are truncated to omit the region of overlap with the tyrosyl radical (Fig. 5). (B) Intensity of the MVFC signal at increasing iron loading in samples of 4.17 µM SynFtn in 100 mM Mes, pH 6.5, frozen 10 s after mixing. Response from the apo protein and protein loaded with 80 Fe2+ per Ftn are shown in black; intermediate loadings (12, 24, and 48 equivalents of Fe2+) are shown in gray. (C) Increase in signal intensity in the high field region (g < 2) assigned to the MVFC in samples of 4.17 µM SynFtn frozen 50–365 ms after mixing with 72 equivalents of Fe2+. Thick traces are the shortest (50 ms) and longest (365 ms) aging times shown, the latter corresponding to maximum signal intensity. Traces at intermediate freezing times are shown in gray. The EPR signal minimum at ∼3,800 G shifts in both sets of spectra, for iron load (B) and reaction time (C), due to increasing relative input of the “minor” MVFC component (A), which has a greater gz value than the “major” one (Table 1). (D) Intensity plots showing the formation and decay of the MVFC (red circles), mononuclear Fe3+ (black squares), and tyrosyl radical (blue triangles) detected by low-temperature EPR spectroscopy over the first 10 s of iron oxidation (72 Fe2+/Ftn) by SynFtn. Solid lines represent fits of the data, yielding apparent first-order rate constants of 3.0 s−1 (MVFC), 2.0 s−1 (Fe3+), and 1.2 s−1 (Tyr radical) for the formation phase, and 0.2 s−1 (MVFC), 0.15 s−1 (Fe3+), and 0.17 s−1 (Tyr radical) for the decay phase. Data for the MVFC can be compared with those for Fe2+ oxidation measured by stopped-flow absorbance at 10 °C (SI Appendix, Fig. S3A), for which apparent first-order rate constants of 8.3 s−1 (rapid phase) and 0.3 s−1 (slow phase) were obtained.